Differences in data volumes
18 February 2024Pandas: indispensable tool for working with data
18 February 2024The transition from unmanaged data flow to its effective integration into business processes starts with converting data from closed formats to open formats.
In scientific research, the principle of sharing open data accelerates discovery and facilitates international collaboration among scientists. In medicine, sharing information between institutions leads to more effective diagnosis and treatment. In information technology, open-source applications allow developers around the world to collaboratively improve software.
A major benefit of open data is its ability to remove the dependence of application developers on specific platforms to access data.
The choice between open and closed data is an obvious one, as is the preference for structured data in automation, data processing and data warehousing processes. Structured data is often used by default in most systems because of its ease of processing and unambiguous interpretation, making it the most preferred type for communication and collaboration at the requirements and business process level.
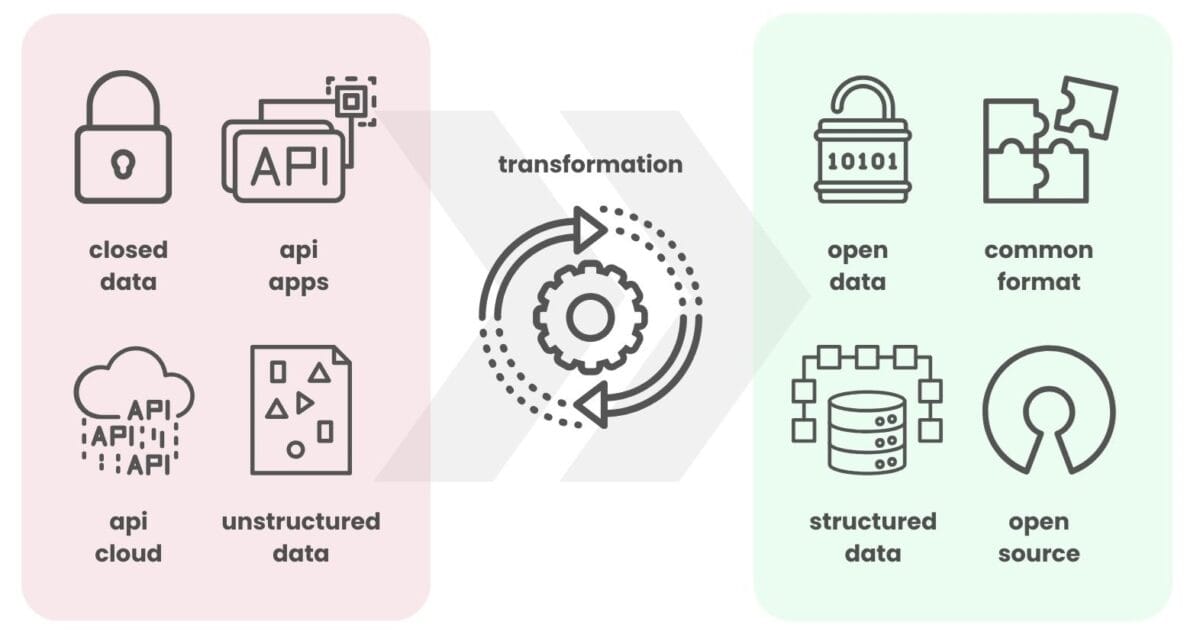
Open and structured data improves automation and collaboration, reducing dependence on specific platforms and accelerating innovation across domains
In the context of the construction industry, open structured data enables smooth and coordinated business processes where teams can focus on optimizing projects rather than struggling with incompatible data formats, platforms and systems.
To transform data into a structured format, a wide range of tools are available, where one of the most popular tools is the Python language library - Pandas.
Due to its flexibility and wide functionality, Pandas has become an indispensable tool for data scientists, automation and analytics professionals, facilitating the process of turning raw data into valuable information. We will use the Pandas library in conjunction with the ChatGPT tool in practical examples in the following chapters of this book, so let's take a closer look at these tools.













