QTO Quantity Take-Off: attribute grouping of data
22 February 2024
QTO calculations using rules from Excel
22 February 2024Translating unstructured data into a structured form significantly improves the efficiency of various processes: it increases the efficiency of data processing and speeds up the validation process by making requirements clear and transparent, as we have already discussed in the previous chapters.
Likewise, moving CAD (BIM) data into a structured form facilitates the attribute grouping process and the QTO process (the transition from CAD (BIM) data to structured data was described in detail in the chapter "Converting CAD (BIM) data to structured form").
A QTO volume attribute table is always a structured table, so by using structured CAD (BIM) data, we can group data by one or more attributes with just one line of code, instead of using tens or hundreds of lines in open-BIM or closedBIM that works with semi-structured mixed geometry and metainformation formats or closed native CAD (BIM) formats.
❏ An example of grouping an entire project by a single attribute. Text request in ChatGPT:
I have a Project as DataFrame - filter the data so “Type” containing the value "Type 1"
➤ ChatGPT Answer:

One line of code written with ChatGPT allows you to group by attribute "Type" and get a group of items of a certain type
And while in the past you had to immerse yourself in learning data analytics to start writing such simple code, now the logic of the process is translated into code via text queries using modern LLM language models such as ChatGPT (more about how ChatGPT helps you automate data processing in the chapter "ChatGPT and LLM for Data Automation").
Automation and LLM language models, such as ChatGPT, can completely free professionals working with grouping and processing CAD (BIM) data from the need to learn programming languages or BIM tools, providing the ability to solve problems through text queries.
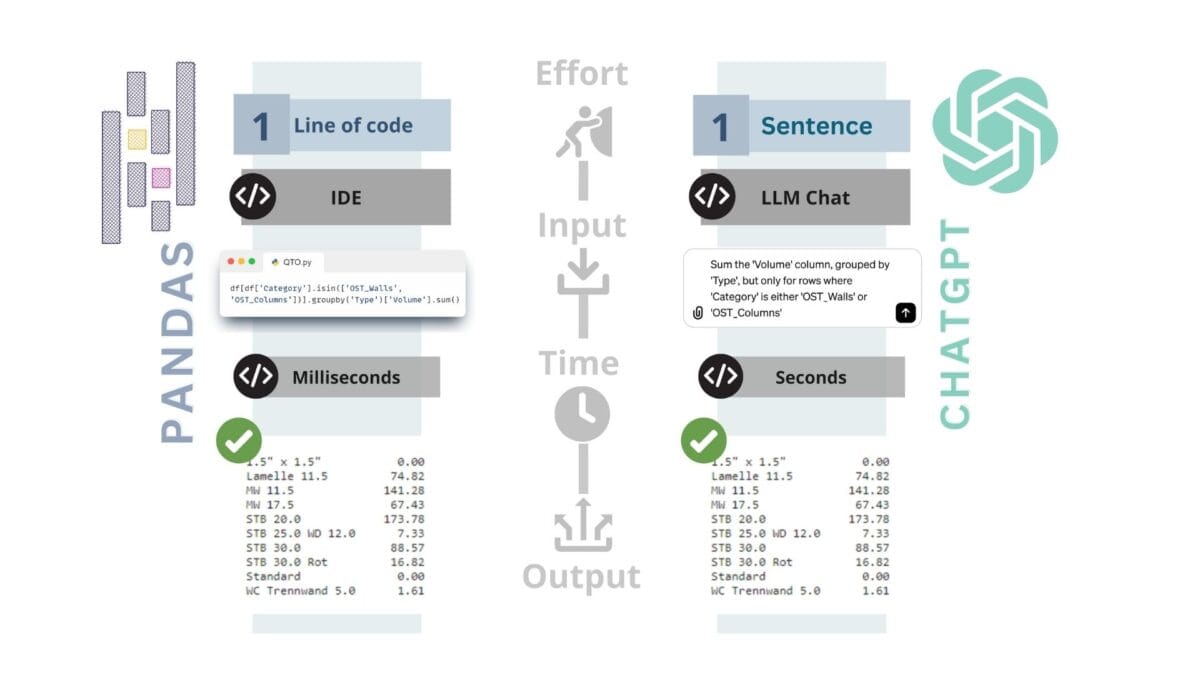
With the use of Pandas and ChatGPT, automation of data processing is now possible through simple text queries
The acquisition of QTO with CAD (BIM) data and the advent of tools such as ChatGPT are transforming traditional approaches to estimating by offering an integrated and rapid method of working to obtain quantitative and volumetric attributes for individual entities and their groups as well as for the entire project.
Now any project manager or engineer can find for example the total volume of all elements of a wall category from a project with hundreds of thousands of elements in a few seconds by writing or speaking a query in one or more sentences.

ChatGPT, working with structured data, understands from the context of a text query what grouping and attributes the user is asking about
In such a simple text query (Figure 3.2-9), the ChatGPT agent processes the text query and summarizes the volume attribute values of all entities of an element with a particular value of the "Category" attribute. The result is a number that represents the total volume attribute in the desired dimension for one specific category (the defined OST_Walls value of the entities in the "Category" attribute).
However, if the estimate as a whole is considered, separate attribute quantities or volumes grouped by individual attributes and their values must be obtained for each kind of work. Typically, estimators and estimators have individual rules for grouping and calculating the total value of quantities and volumes for each group of items. To simplify the generation of values for all groups, queries are not written as text queries, but as tables that describe the grouping rules for the groups of entities in the project.














