Musical compositions are made up of notes that combine to create complex pieces of music, while words are created from a primitive unit, the letter-sound. Whether it is nature, science, economics, art or technology, the world shows a remarkable unity and harmony in its quest for destruction, structure, cyclicity and creation.
In the same way, processes in costing systems are broken down into the smallest structured units - resource items - at the level of calculations and scheduling. These units are then used to form more complex calculations and schedules. CAD (BIM) systems work on the same principle, where complex architectural and engineering projects are built from basic elements - individual smallest elements or library components, from which a full 3D model of a complex building or structure is created.
The smallest elements with their finite indivisibility are the basic building blocks in all business processes. It is important to carefully consider from the very beginning how to collect and store these smallest building blocks from different sources. Decisions will also have to be made between approaches such as data warehouses (DWH) and data lakes (Data Lakes). These issues first arose in the telecoms industry, then became relevant for financial organisations, and now companies in the construction industry will face similar issues.
The concept of cyclicality and structure found in nature and science is also reflected in the modern world of data. Just as in nature all living things return to atoms and molecules, so in the world of modern data processing tools, information tends to move to the most primitive, molecular form possible.
This idea is embodied in the Data Lakehouse architecture, where data, like drops of water, merge into a single entity, forming a "lake" of heterogeneous information. The development of the Data Lakehouse concept represents an evolutionary step in the field of data management, emerging at the intersection of Data Warehouses and Data Lakes.
- In traditional Data Warehouses, data is typically pre-processed, transformed and cleaned (ETL - Extract, Transform, Load) before it is loaded into the warehouse. This implies that the data is structured and optimized for specific analytics and reporting tasks. The main focus is on maintaining high query performance and data integrity. However, this approach can be costly and less flexible in terms of integrating new data types and rapidly changing data schemas.
- Data Lakes, on the other hand, are designed to store large amounts of raw data in its original format. The ETL process is being replaced by ELT (Extract, Load, Transform), where data is first loaded into storage "as is" and only then can it be transformed and analyzed as required. This provides greater flexibility and the ability to store heterogeneous data, including unstructured data such as text, images and logs. The downside can be more complex query performance optimization and data management.
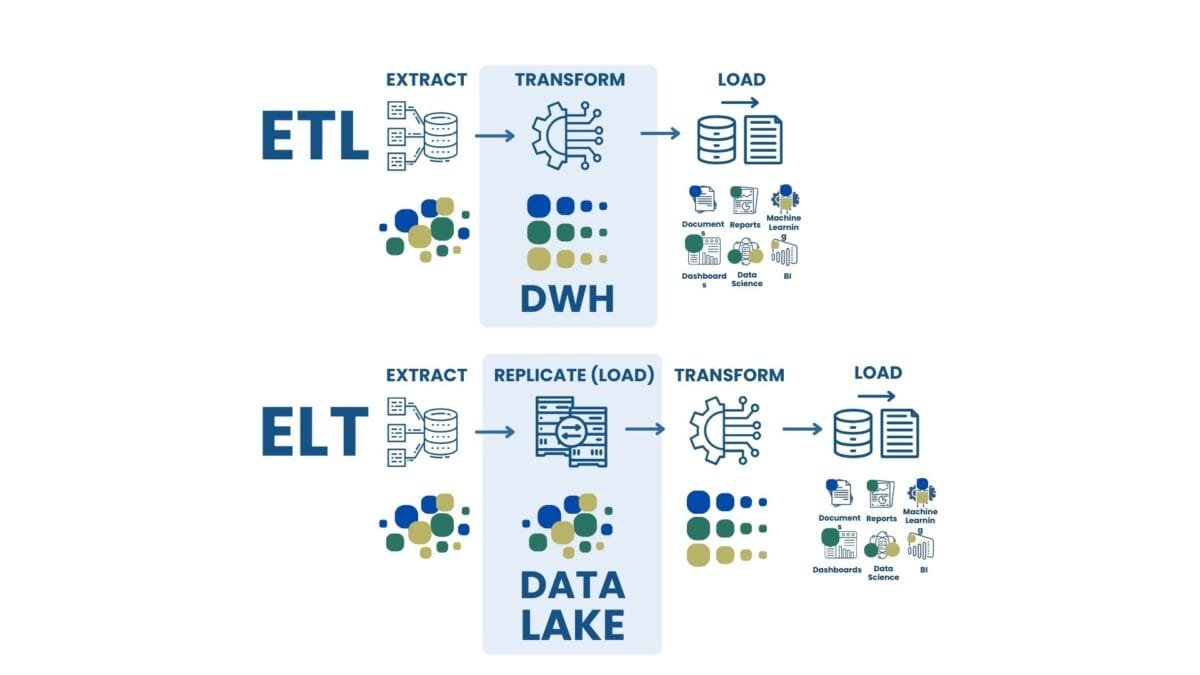
Traditional Data Warehouses focus on pre-processing data for high query performance, whereas Data Lakes prioritize flexibility by storing raw data and transforming it as needed
Traditional Data Warehouses, designed to store structured data in a format optimized for analytical queries, faced limitations in handling unstructured data and scalability. In response to these challenges, Data Lakes have emerged, offering flexible storage for large amounts of heterogeneous data.
Data Lakehouse is an architectural approach that seeks to combine the flexibility and scalability of Data Lakes with the manageability and query performance of Data Warehouses. Key features of Data Lakehouse include:
- Open storage format: The use of open formats for data storage, such as Parquet (Apache), provides efficiency and query optimization.
- Read-only schema: Unlike the traditional write-only schema approach in DWH, Lakehouse supports read-only schema, allowing more flexibility in managing data structure.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Supports storage and analysis of both structured and unstructured data, while providing high query performance through storage-level optimization.
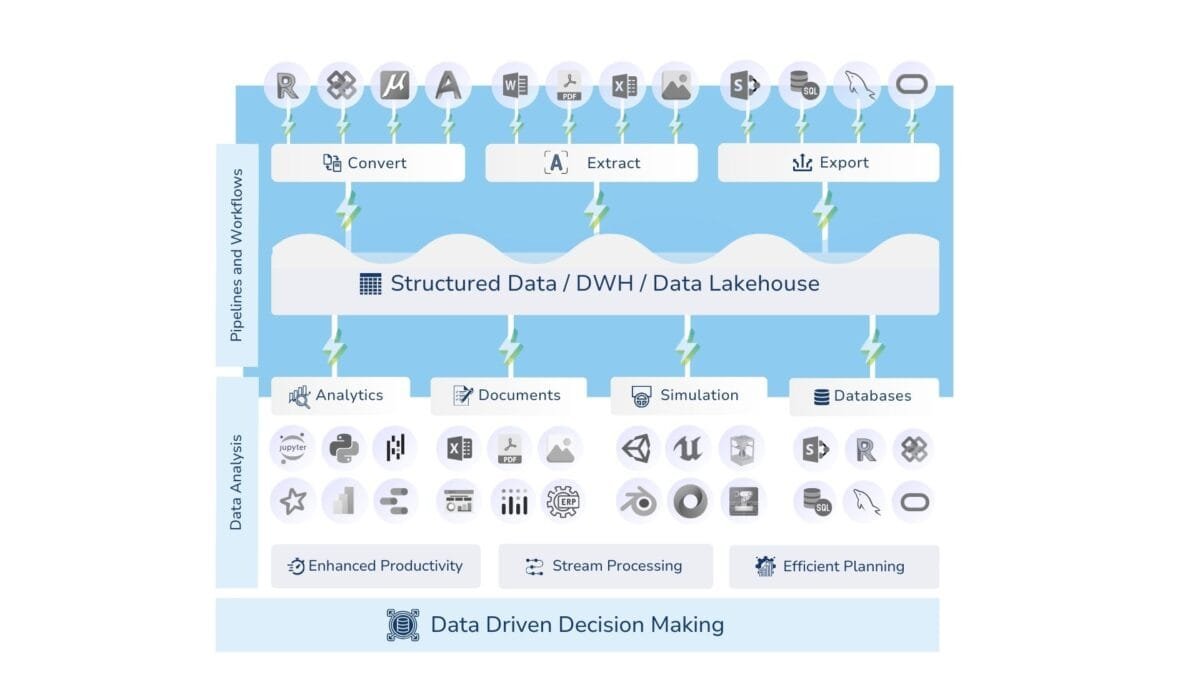
Today's data world seeks to transform information into a simple form from different data architectures
Thus, Data Lakehouse offers a compromise solution that combines the advantages of both approaches, making it ideal for modern analytical workloads that require flexibility in processing
Data Lakehouse is a synthesis of data lakes and data warehouses, combining the flexibility and scalability of the former with the query manageability and optimization of the latter.
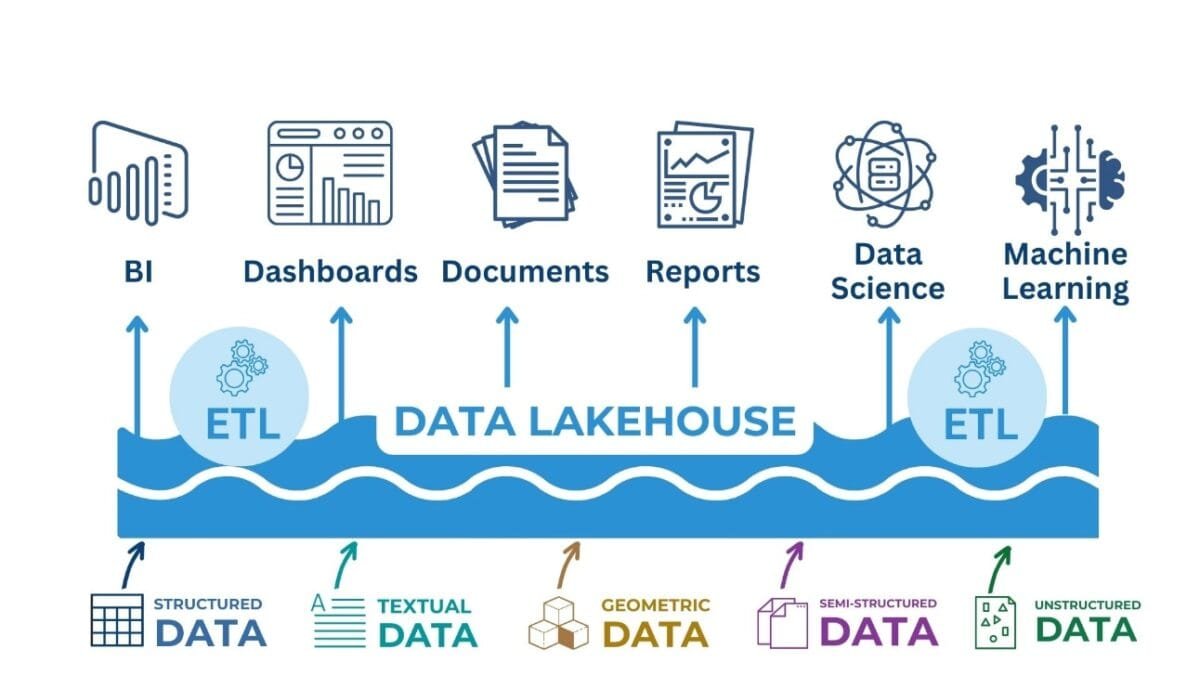
Data Lakehouse is the next generation of storage designed to meet today's complex and ever-changing automation, analytics, and machine learning requirements in construction
Before data storage and infrastructure can be developed, Data Governance policies and standards must first be developed and approved at the data governance level.

















