Pandas library, occupies a special place in the arsenal of tools for working with data, becoming one of the most popular and demanded in this area.
In the world of analytics and structured data management, Pandas stands out for its simplicity, speed and power, providing users with a wide range of tools to effectively analyze and process information.
The Python programming language's Pandas library not only allows to perform basic operations such as reading and writing tables, but also to perform more complex tasks, including merging data, grouping data, and performing complex analytical calculations. Pandas can be compared to a Swiss knife for data analysts and data engineers.
As of January 2024, the number of downloads of the Pandas library is about 4.3 million per day.
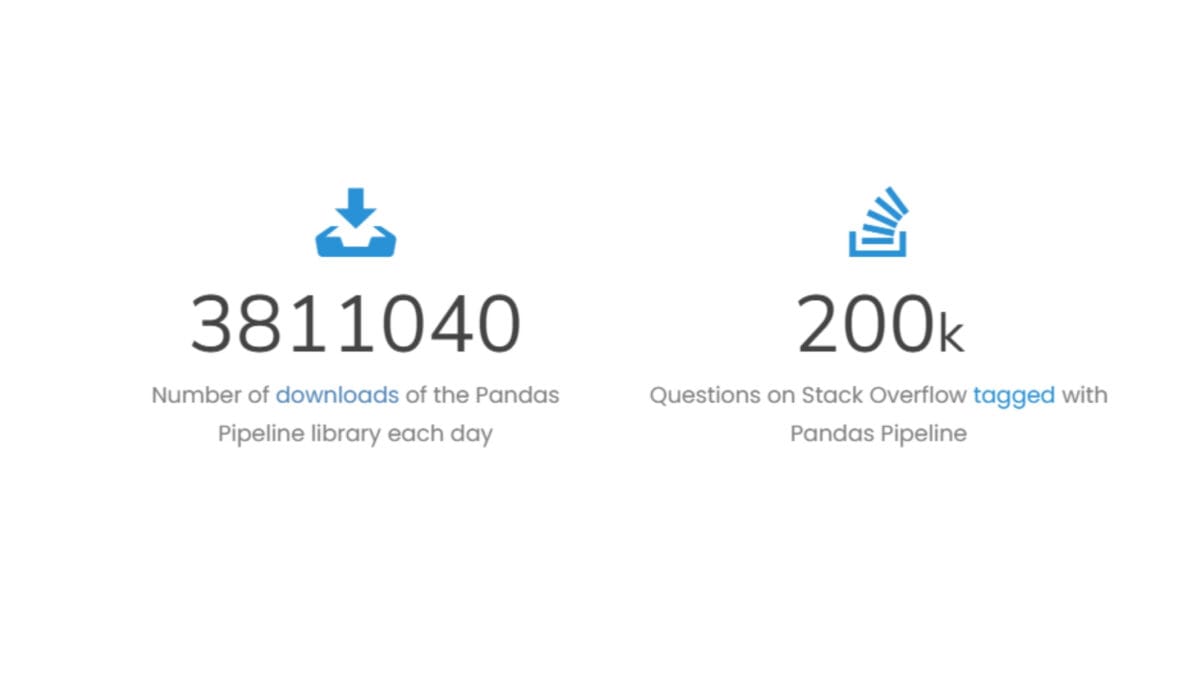
The Pandas data tool is one of the most popular libraries for transforming, analysing and processing data
The query language in the Pandas library is similar in its functionality to the SQL query language we discussed in the chapter "Relational Databases and SQL Query Language".
Both tools offer powerful data manipulation capabilities including sampling, filtering, sorting and grouping data. Pandas is often preferred in scientific research, process automation, Pipeline creation, and Python data manipulation, while SQL is the standard in database management and is often used in enterprise environments to work with large amounts of data.
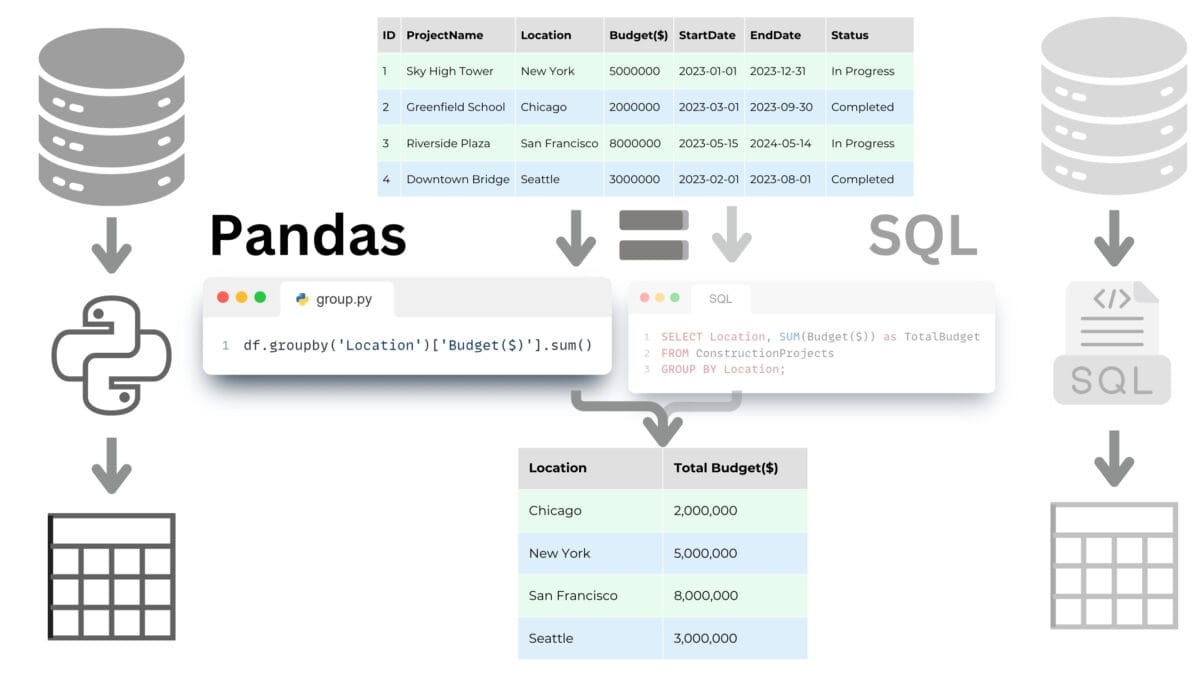
Pandas, unlike SQL, has the flexibility to handle a variety of data formats, not limited to databases
Using Pandas, it is possible to work efficiently with large amounts of data - much larger than what Excel can handle. Even when millions of rows are involved, Pandas can handle such tables with ease, providing powerful tools for analyzing, visualizing, and gaining valuable insights from the data. In addition, Pandas has strong community support: hundreds of millions of developers and analysts (Kaggle.com, Google Collab, Microsoft Azure Notebooks, Amazon SageMaker) around the world use it daily online or offline, providing a large number of out-of-the-box solutions for any business desire.

















