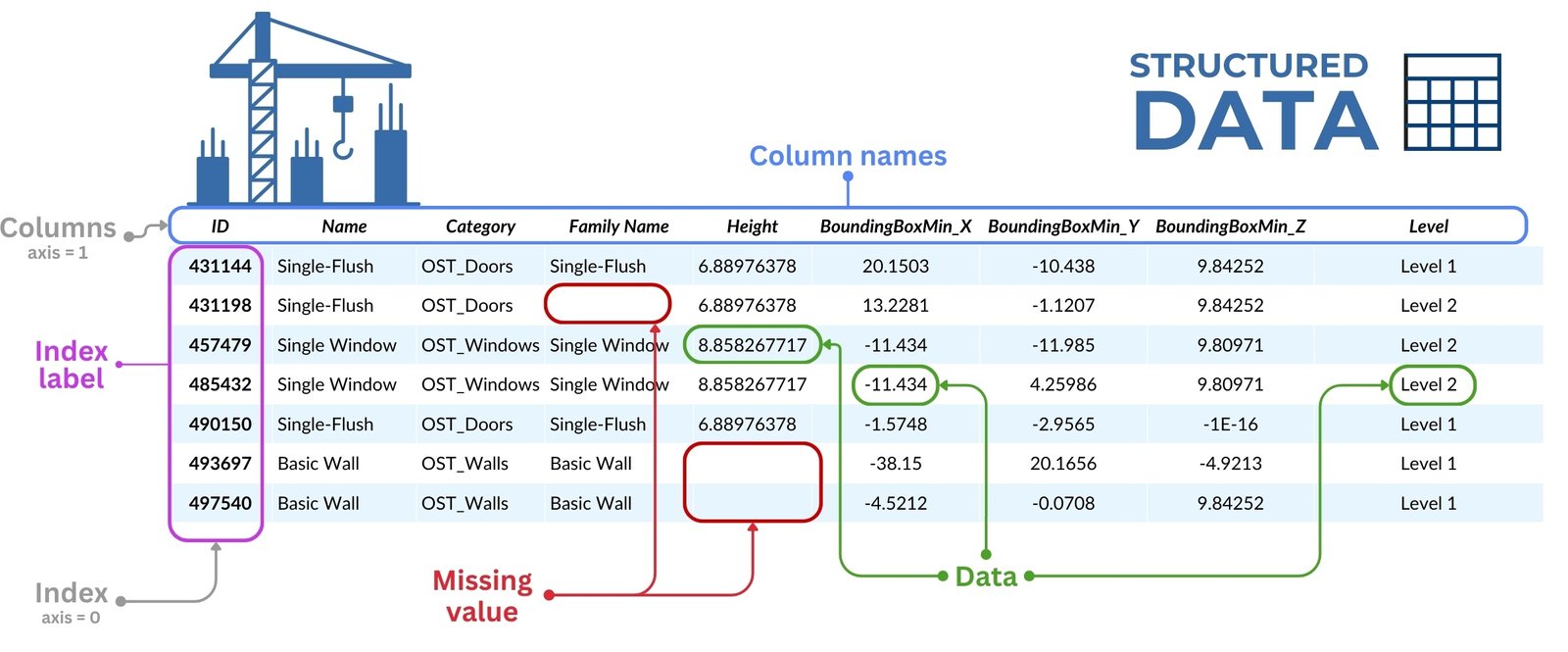
DataFrame is the central structure in the Pandas library, which is a two-dimensional table (Fig. 3.4-6) where rows correspond to individual objects or records and columns correspond to their characteristics, parameters, or categories. This structure visually resembles Excel spreadsheets, but is far superior in terms of flexibility, scalability, and functionality.
A DataFrame is a way to represent and process tabular data stored in the computer’s RAM.
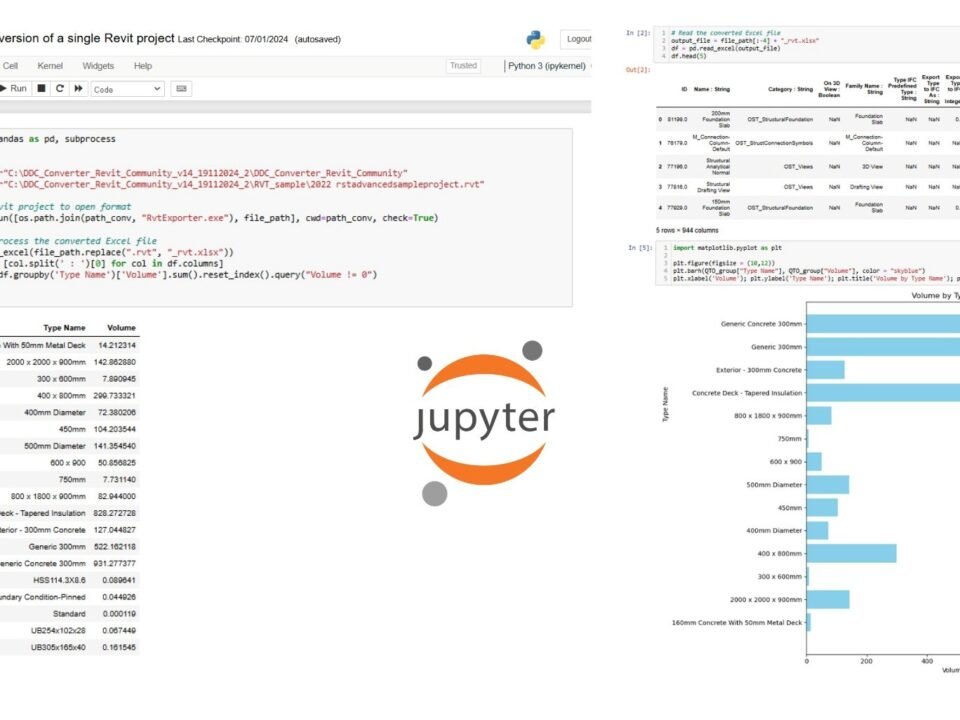
DataFrame is a way of representing and processing tabular data stored in the computer’s RAM. In a table, rows can reflect, for example, elements of a construction project, and columns – their properties: categories, dimensions, coordinates, cost, terms and so on. Moreover, such a table can contain both information on one project (Fig. 4.1-13) and data on millions of objects from thousands of different projects (Fig. 9.1-10). Thanks to vectorized Pandas operations, it is easy to filter, group and aggregate such volumes of information at high speed.
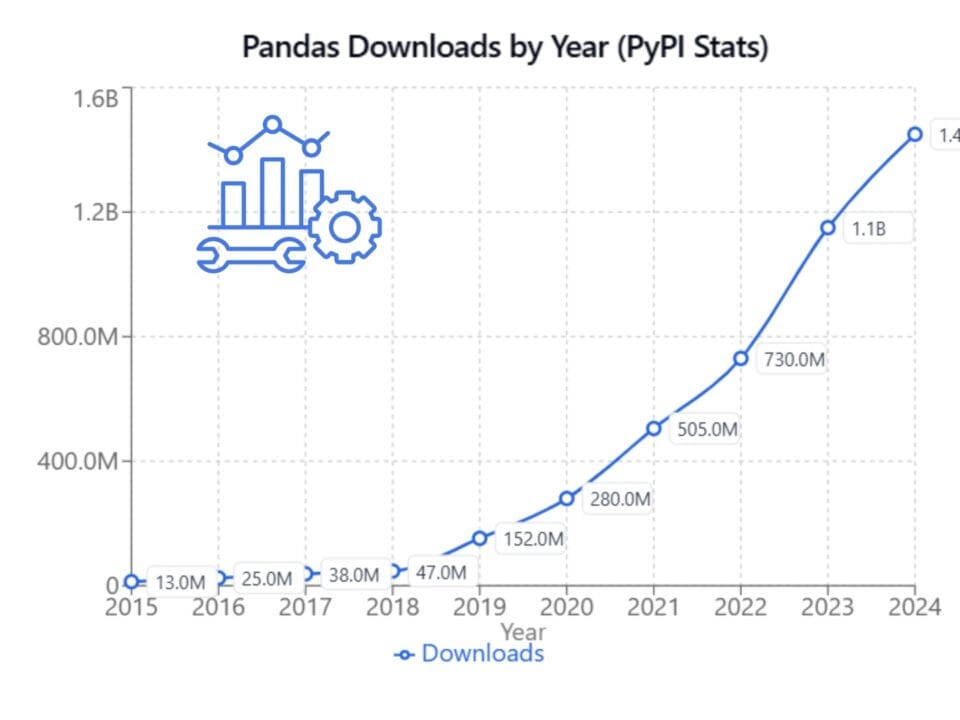
Nvidia estimates that already today up to 30% of all computing resources are used to process structured data – dataframes, and this share continues to grow.
Data processing is what probably one third of the world’s computing is done in every company. The data processing and data of most companies are in DataFrame, in table format
– Jensen Huang, CEO of Nvidia (“NVIDIA CEO Jensen Huang Keynote at COMPUTEX 2024,” June 2, 2024)
Let’s list some key features of DataFrame in Pandas:
- Columns: in DataFrame, data is organized into columns, each with a unique name. Attribute columns can contain data of different types, similar to columns in databases or columns in tables.
- Pandas Series is a one-dimensional data structure in Pandas, similar to a list or column in a table, where each value corresponds to a different index
Pandas Series has over 400 attributes and methods, making working with data incredibly flexible. You can directly apply one of the four hundred available functions to a column, perform math operations, filter data, replace values, work with dates, strings, and more. In addition, Series supports vectorized operations, which greatly speeds up the processing of large datasets compared to cyclic calculations. For example, you can easily multiply all values by a number, replace missing data, or apply complex transformations without writing complicated loops.
- Rows: in DataFrame can be indexed with unique values. This index allows you to quickly change and adjust the data in specific rows.
- Index: By default, when you create a DataFrame Pandas assigns each row an index from 0 to N-1 (where N is the number of all rows in the DataFrame). However, the index can be changed to include special designations such as dates or unique characteristics.
- Indexing rows in a DataFrame means that each row is assigned a unique name or label, which is called the DataFrame index.
- Data Types: DataFrame supports a variety of data types, including:
int,float,bool,datetime64andobectfor text data. Each DataFrame column has its own data type that determines what operations can be performed on its contents. - Data operations: DataFrame supports a wide range of operations for data processing, including aggregation (
groupby), merge (mergeandjoin), concatenation (concat), split-apply-combine, and many other data transformation techniques. - Size Manipulation: DataFrame allows you to add and remove columns and rows, making it a dynamic structure that can be modified according to your data analysis needs.
- Visualizing data: using built-in visualization techniques or interacting with popular data visualization libraries such as Matplotlib or Seaborn, DataFrame can be easily converted to graphs and charts to present data graphically.
- Data input and output: Pandas provides functions to read import and export data to various file formats such as CSV, Excel, JSON, HTML and SQL, potentially making DataFrame a central hub for data collection and distribution.
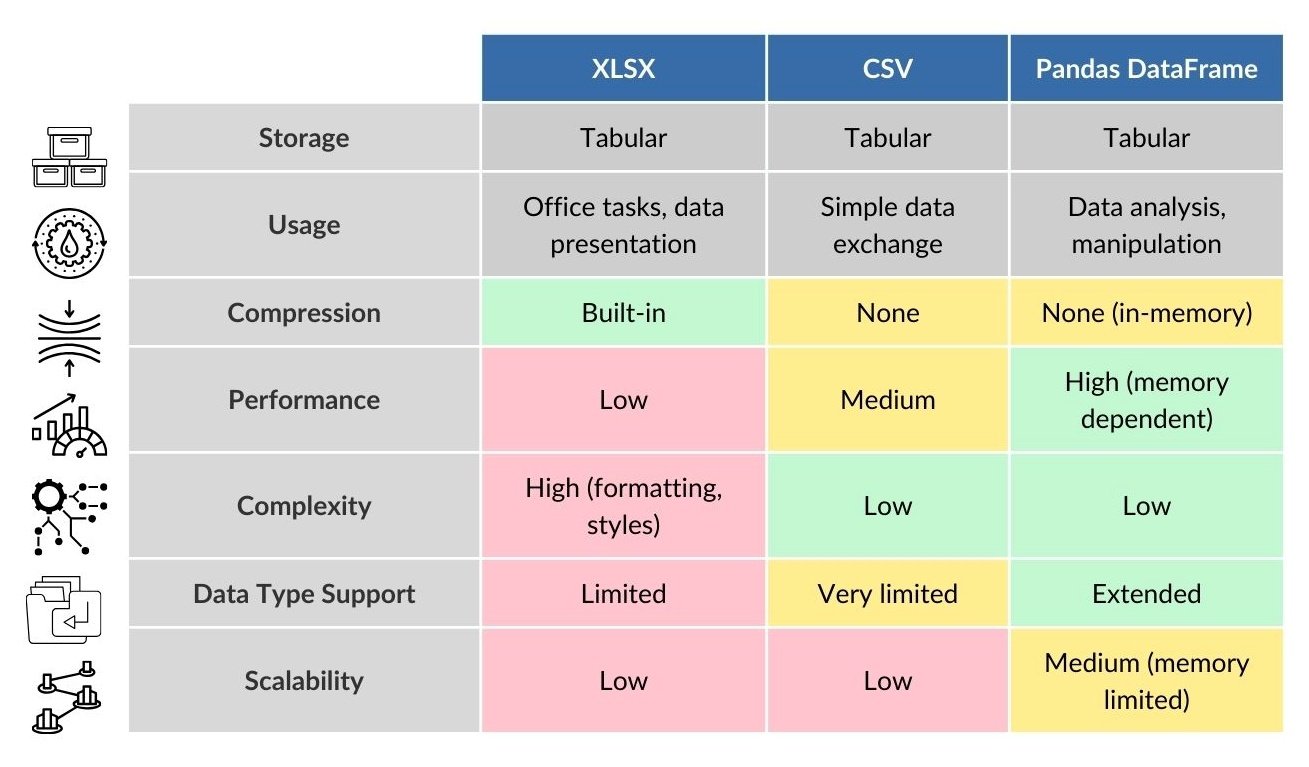
Unlike CSV and XLSX, Pandas DataFrame provides greater flexibility and performance when working with data: it can handle large amounts of information in RAM, supports extended data types (including dates, logical values, and time series), and provides extensive capabilities for filtering, aggregating, merging, and visualizing data. While CSV does not store information about data types and structure, and XLSX is often overloaded with formatting and has low scalability, DataFrame remains the optimal choice for rapid analytics, process automation, and integration with AI -models (Fig. 3.4-7). In the following chapters we will explore each of these aspects of data in detail, also in Part 8 of the book, similar formats such as Parquet, Apache Orc, JSON, Feather, HDF5 and data warehouses will be discussed in detail (Fig. 8.1-2).
Because of their flexibility, power, and ease of use, the Pandas library and DataFrame format have become the de facto standard in Python data analysis. They are ideal for both creating simple reports and building complex analytic pipelines, especially in conjunction with LLM models.
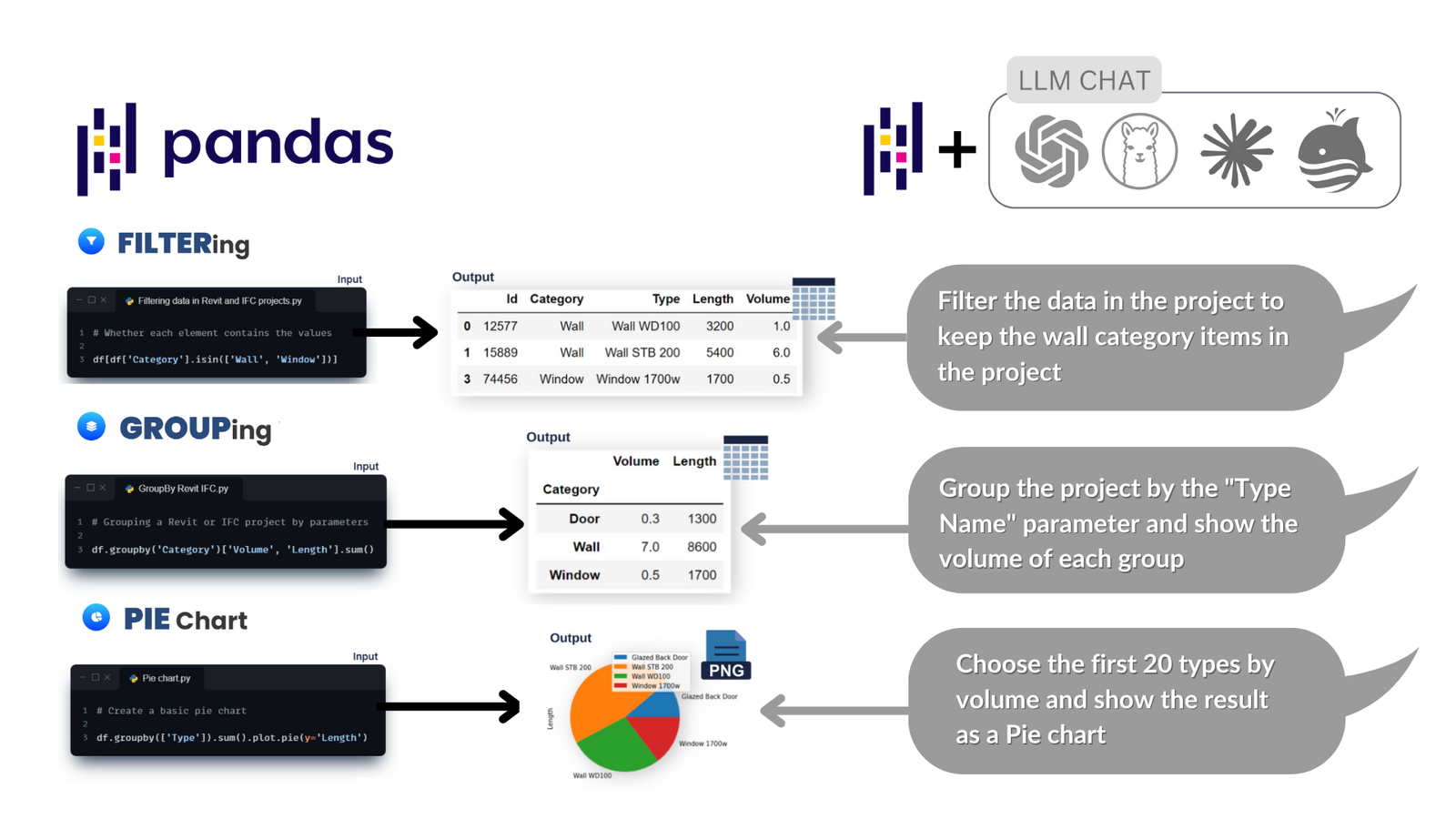
Today Pandas is actively used in LLM-based chat rooms such as ChatGPT, LlaMa, DeepSeek, QWEN and others. In many cases, when a model receives a query related to table processing, data validation or analytics, it generates code exactly using the Pandas library. This makes DataFrame a natural “language” for representing data in AI dialogs (Fig. 3.4-8).
Modern data technologies such as Pandas make it easier to analyze, automate and integrate data into business processes. They deliver results quickly, reduce the workload of specialists, and ensure repeatable operations.