In addition to PDF documents with tables (Fig. 4.1-2) and scanned versions of tabular forms (Fig. 4.1-5), a significant part of information in project documentation is presented in text form. It can be both coherent sentences in text documents and fragmentary records scattered over drawings and schemes. In modern conditions of data processing one of the most common tasks is to convert such text into a structured format suitable for analysis, visualization and decision making.
Central to this process is taxonomy, a classification system that organizes information into categories and subcategories based on common features.
A taxonomy is a hierarchical classification structure used to group and organize objects. In the context of text processing, it serves as a basis for systematically categorizing items into semantic categories, thus simplifying analysis and improving the quality of data processing.
Taxonomy creation is accompanied by the steps of entity extraction, categorization and contextualization. To simulate the process of extracting information from textual data, we need to perform the following steps, similar to those we have already applied to structuring data from PDF documents:
- Data extraction (Extract): you need to analyze text data to extract information about delays and changes in the project schedule.
- Categorization and Classification (Transofrm): categorize the information received, e.g. Reasons for delays and schedule changes.
- Integration (Load): at the end we prepare structured data for integration into external data management systems.
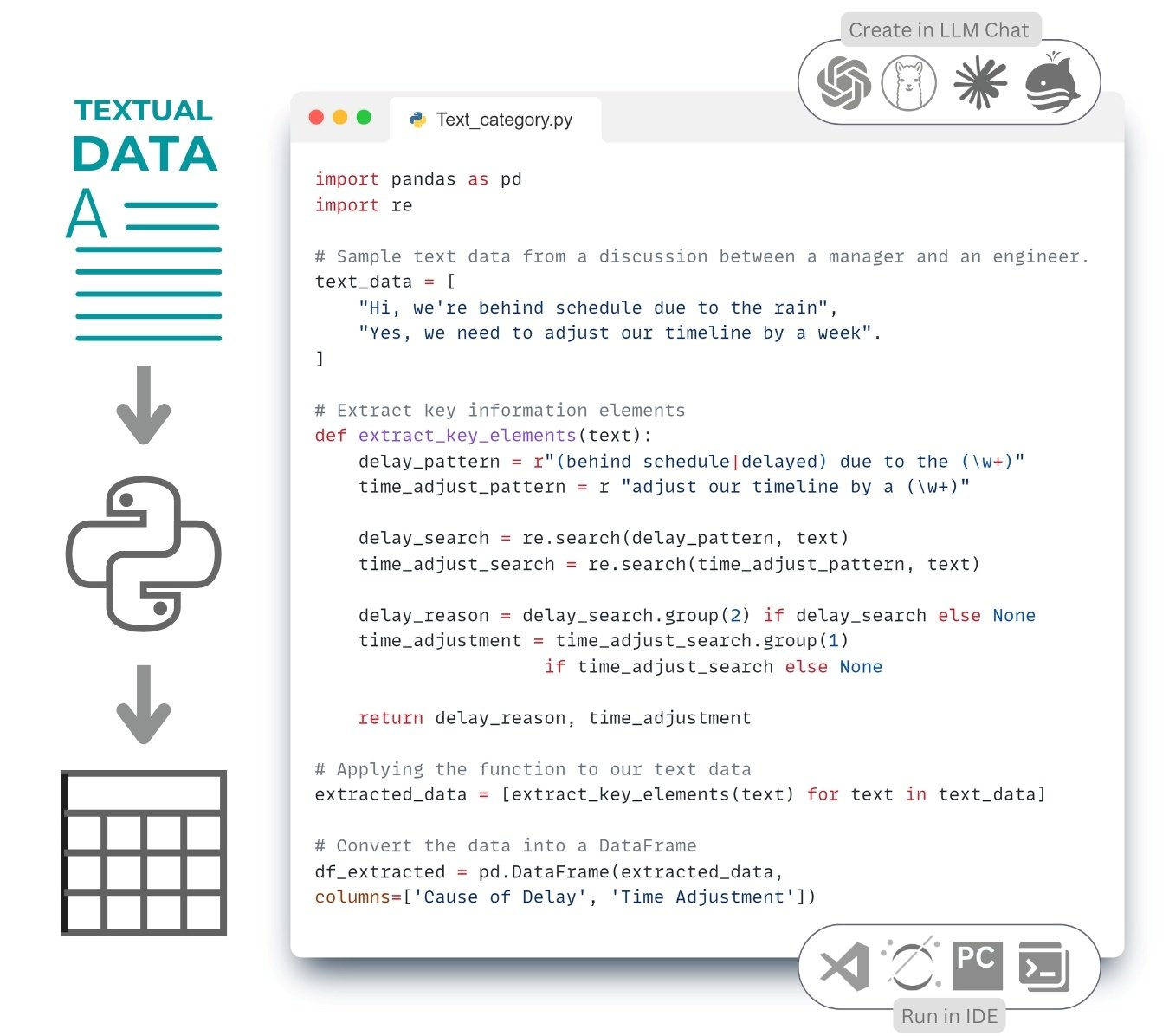
Consider a situation: we have a dialog between a project manager and an engineer discussing problems with the schedule. Our goal is to extract the key elements (reasons for delay, schedule adjustments) and present them in a structured way (Fig. 4.1-7).
Let’s perform the extraction based on the expected keywords, create a DataFrame to simulate data extraction and after transformation, a new DataFrame table that will contain columns for date, event (e.g., reason for delay) and action (e.g., schedule change).

Here is the code to solve the problem using a text query in one of the language models as in the previous examples.
- Send a text request to any LLM chat room:
I have a conversation between a manager, “Hello, we are behind schedule due to rain” and an engineer, “Yes, we need to adjust the deadline by a week”. I need a script that will analyze future similar text conversations, extract the reasons for delays and necessary deadline adjustments, and then generate a DataFrame from that data. The DataFrame should then be saved to a CSV -file ⏎
In this example (Fig. 4.1-7), text data containing correspondence between a project manager and an engineer is analyzed to identify and extract specific information that may affect the management of future projects with similar dialogs. Using regular expressions (we’ll talk more about regular expressions in the chapter “Structured Requirements and RegEx Regular Expressions “), the causes of project delays and necessary adjustments to the time schedule are identified through patterns. The function written in this example extracts either the cause of delay or the time adjustment from the strings based on the patterns: highlighting the word after “because of” as the cause of delay or the word after “by” as the time adjustment.
If a row mentions a delay due to weather, “rain” is identified as the cause; if a row mentions a schedule adjustment for a specific period, that period is extracted as a time adjustment (Fig. 4.1-9). The absence of any of these words in a row results in a value of “None” for the corresponding attribute-column.
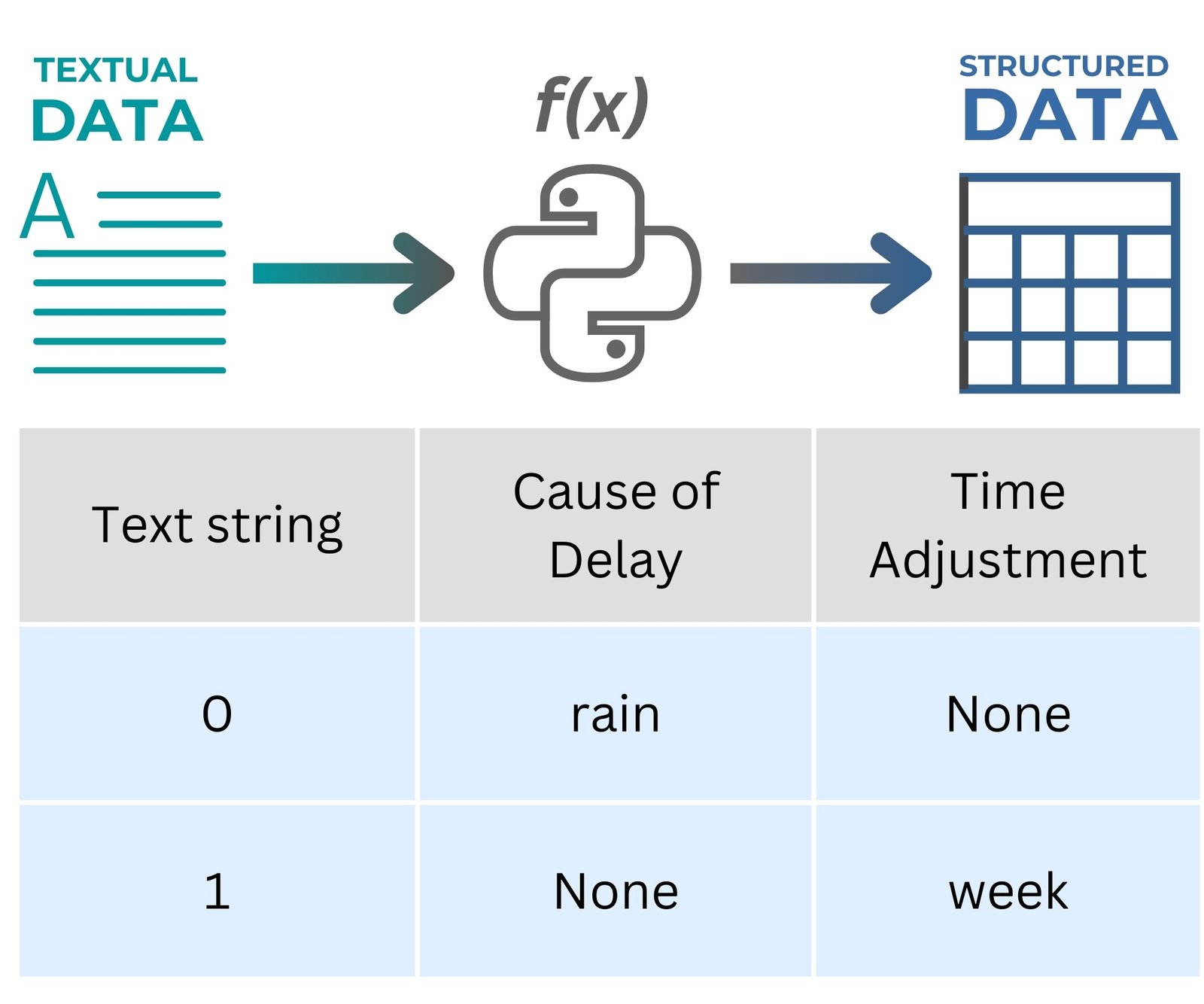
Structuring and parameterization of conditions from the text (dialog, letter, document) allows to promptly eliminate delays in construction: for example, lack of workers can affect the pace of work in bad weather, so companies, knowing the delay parameters from dialogs (Fig. 4.1-9) between the foreman at the construction site and the project manager – in advance can strengthen the crew in case of an unfavorable forecast.
Converting documents and images into a structured format can be achieved with relatively simple, open and free categorization-based tools.
Element categorization is also a key part of working with project data, especially in the context of using CAD software (BIM).