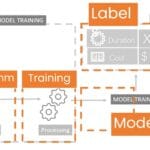
Estimation of construction time and cost is one of the key processes in the activities of a construction company. Traditionally, such estimates are made by experts based on experience, reference books and regulatory databases. However, with digital transformation and increasing data availability, it is now possible to use machine learning (ML) models to improve the accuracy and automation of such estimates.
The introduction of machine learning into the process of calculating the cost and timing of construction not only makes it possible to increase the efficiency of planning, but also becomes a starting point for integrating intelligent models into other business processes – from risk management to optimizing logistics and procurement.
It is important to be able to quickly determine how long it will take to build a project and what its total cost will be. These questions about project time and cost have traditionally been at the forefront of the minds of both clients and construction companies since the birth of the construction industry.
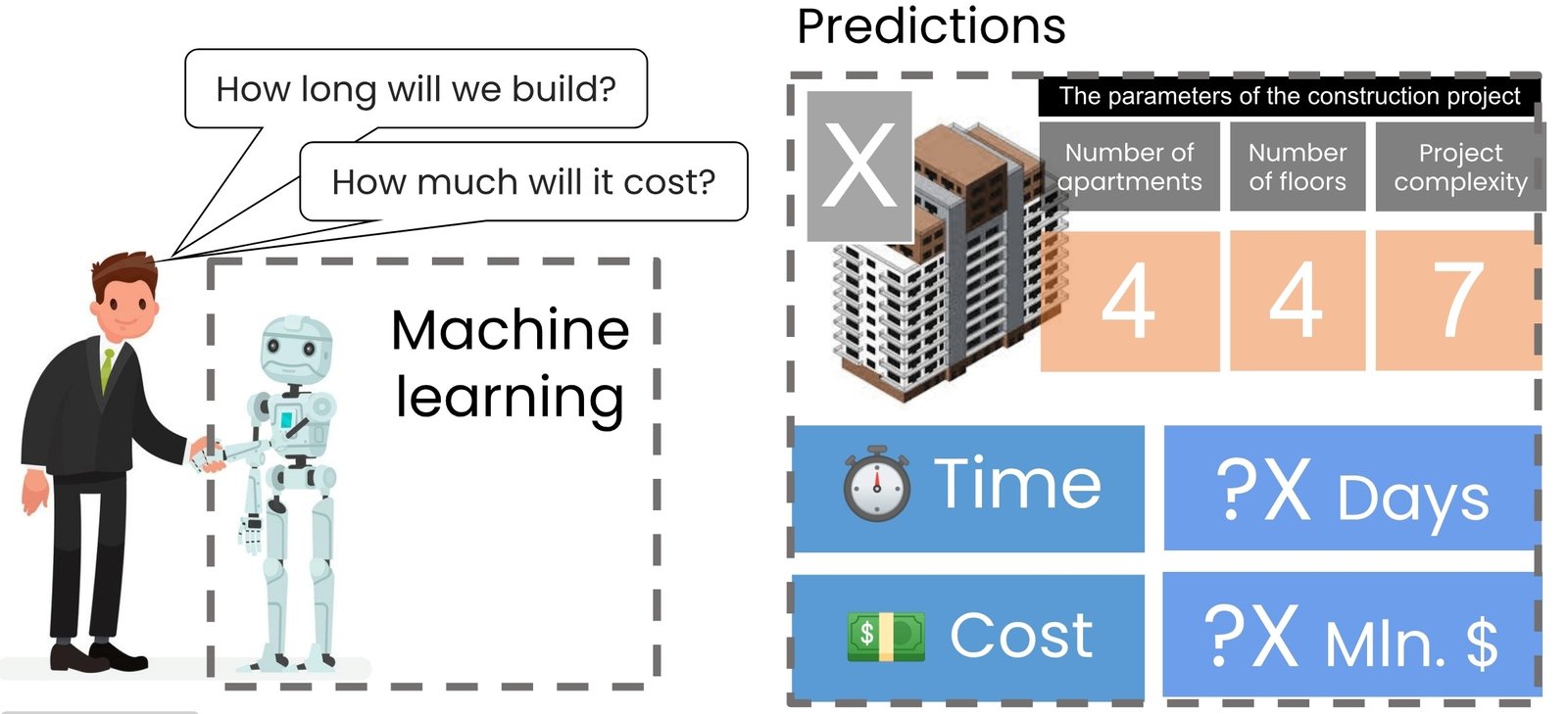
In the following example, key data from past projects will be extracted and used to develop a machine learning model, which will allow us to use the model to estimate the cost and timing of new construction projects with new parameters (Fig. 9.3-1).
Consider three projects with three key attributes: the number of apartments (where 100 apartments is equivalent to the number 10 for ease of visualization), the number of floors, and a conditional measure of construction complexity on a scale of 1 to 10, where 10 is the highest complexity score. In machine learning, the process of converting and simplifying values such as 100 to 10 or 50 to 5 is called “normalization”.
Normalization in machine learning is the process of bringing different numerical data to a common scale to facilitate its processing and analysis. This process is especially important when the data has different scales and units.
Suppose that the first project (Fig. 9.3-2) had 50 apartments (after normalization, 5), 7 floors and a complexity score of 2, which meant a relatively simple construction. The second project already had 80 apartments, 9 floors and a relatively complex project. Under these conditions, construction of the first and second apartment building took 270 and 330 days, and the total project cost was $4.5 million and $5.8 million, respectively.
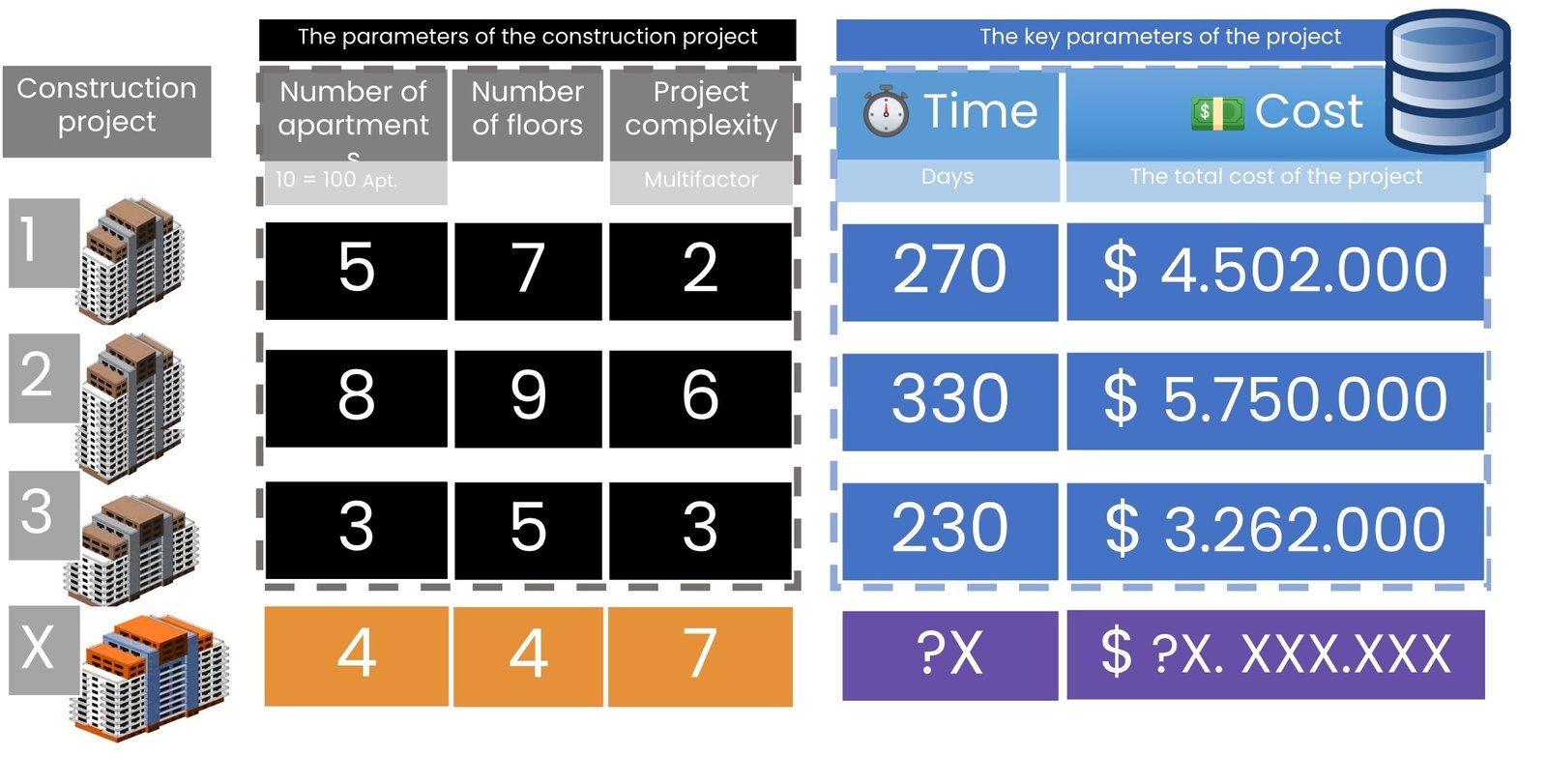
When building a machine learning model for such data, the main task is to identify critical attributes (or labels) for prediction, in this case, construction time and cost. With a small dataset, we will use information about previous construction projects to plan new ones: using machine learning algorithms, we have to predict the construction cost and duration of a new project X based on given attributes of the new project, such as 40 apartments, 4 floors, and a relative high project complexity of 7 (Fig. 9.3-2). In a real-world setting, the number of input parameters can be much larger, ranging from several tens to hundreds of factors. These may include: type of construction materials, climatic zone, qualification level of contractors, availability of utilities, type of foundation, season of commencement of works, comments of foremen, etc.
To create a predictive machine learning model, we need to choose an algorithm to create it. An algorithm in machine learning is like a mathematical recipe that teaches the computer how to make predictions (mix in the right order of parameters) or make decisions based on data.
To analyze data on past construction projects and predict the timing and cost of future projects (Fig. 9.3-2), one popular machine learning algorithm can be used:
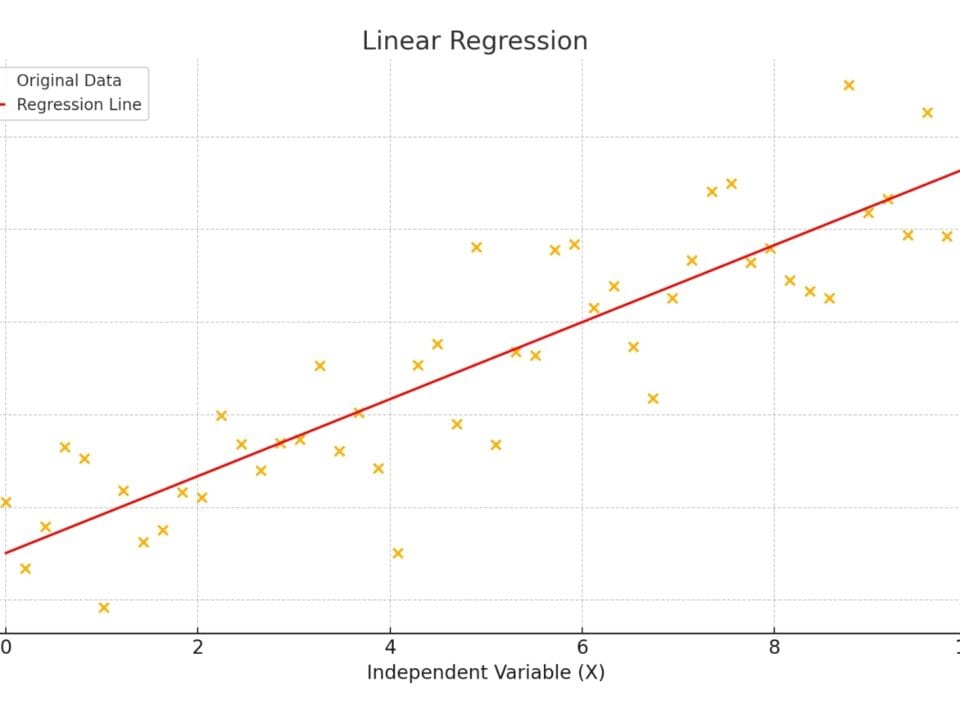
- Linear regression (Linear regression): this algorithm tries to find a direct relationship between attributes, for example between the number of floors and the construction cost. The goal of the algorithm is to find a linear equation that best describes this relationship, which allows making predictions.
- Algorithm k-nearest neighbors (k-NN): this algorithm compares a new project with past projects that were similar in size or complexity. The k-NN classifies the data based on which of the k (number) training examples are closest to it. In the context of regression, the result is the mean or median of the k nearest neighbors.
- Decision Trees: is a predictive modeling model that divides data into subsets based on different conditions using a tree structure. Each node of the tree represents a condition or question leading to further division of the data, and each leaf represents the final prediction or outcome. The algorithm divides the data into smaller groups based on different characteristics, such as first by number of stories, then by complexity and so on, to make a prediction.
Let’s take a look at machine learning algorithms for estimating the cost of a new project using two popular algorithms as examples: linear regression and the K-nearest neighbors algorithm.