The era of modern digital data storage and processing began with the advent of magnetic tape in the 1950s, which opened up the possibility of storing and utilizing large amounts of information. The next breakthrough was the advent of disk drives, which radically changed the approach to data management in the construction industry.
With the development of data warehousing, a large number of companies have entered the solution market and started developing modular software to create, store, process data and automate routine tasks
The exponential growth of information and tools has led to the need for integrated, modular solutions that don’t work with individual files, but help manage and control the flow of data across processes and projects.
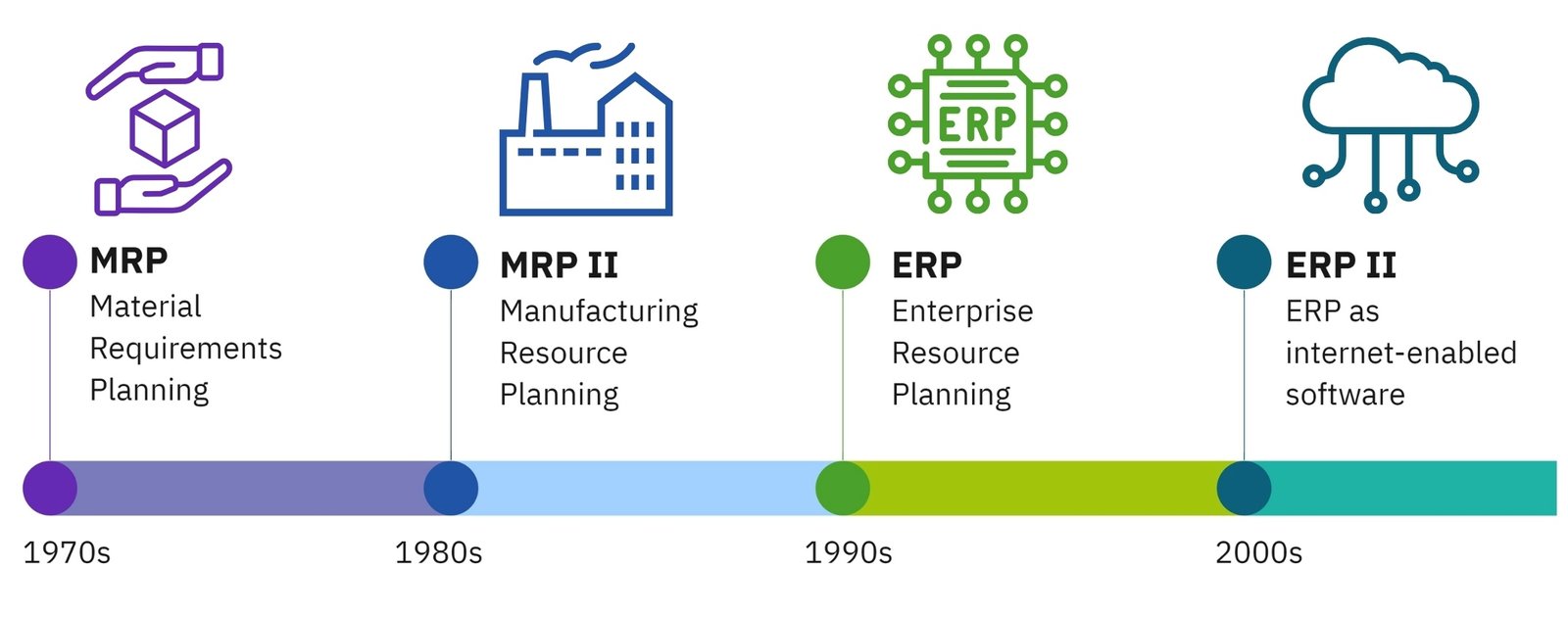
The first comprehensive platform tools had to not only store documents, but also document all change requests and operations in processes: who initiated them, what was the scope of the request, and what was finally recorded as a value or attribute. For these purposes, a system was needed that could track accurate calculations and decisions made (Fig. 1.2-1). Such platforms were the first MRP (Material Requirements Planning) and ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems that gained popularity since the early 1990s (И. McCue, “History of ERP,” 2024)]
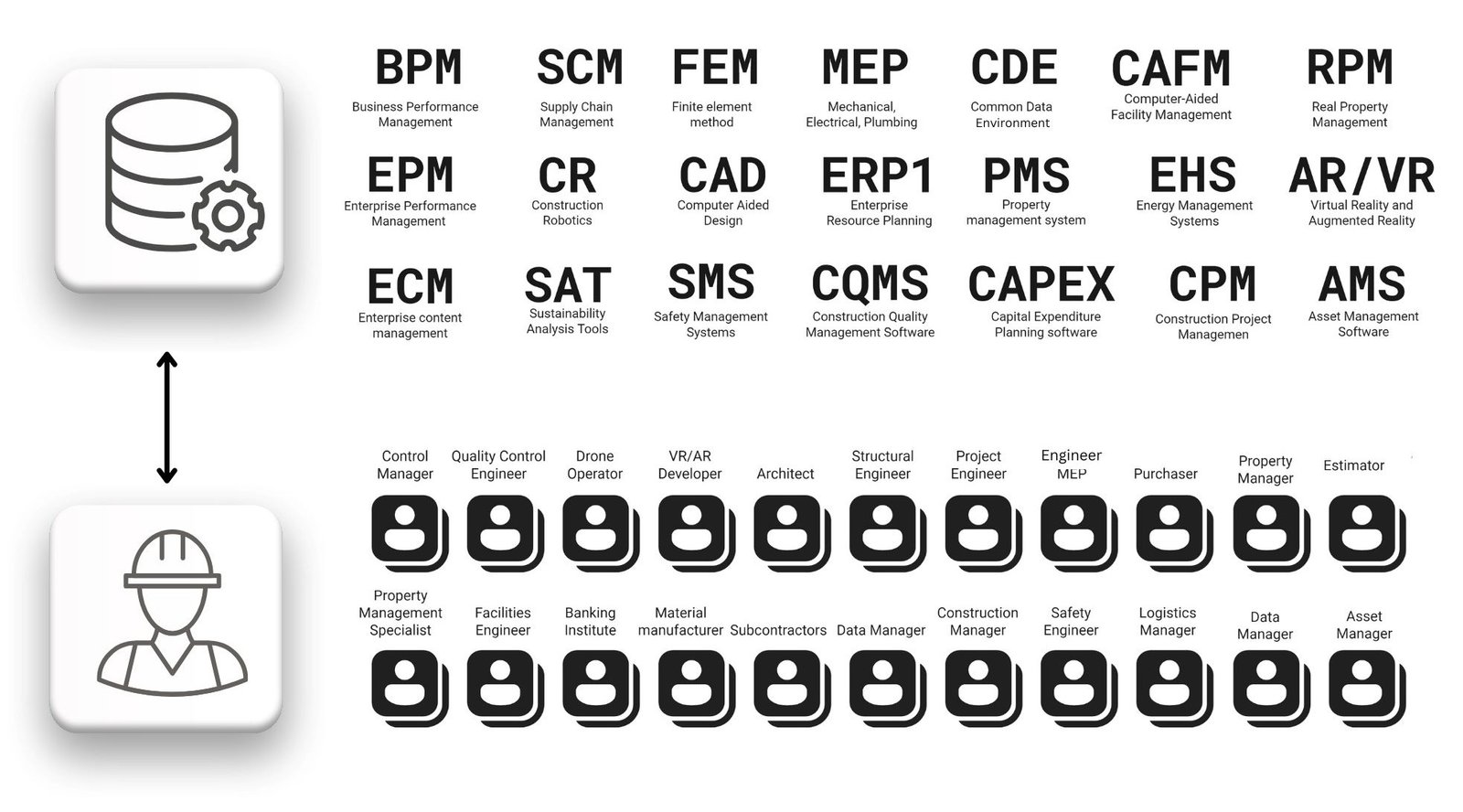
The first MRP – and ERP – systems laid the foundation for the digitalization era in business process and construction project management. Modular systems, originally designed to automate key business processes, have over time become integrated with additional, more flexible and adaptive software solutions.
These additional solutions were designed for data processing and project content management (Fig. 1.2-2), they either replaced certain modules of large systems, or effectively complemented them, extending the functionality of the entire system.
Over the past decades, companies have invested heavily in modular systems (erpscout, “ERP Price: How much does an ERP system cost?”), perceiving them as long-term integrated solutions.
According to the Software Path report for 2022 (softwarepath, “What 1,384 ERP projects tell us about selecting ERP (2022 ERP report),” 18 Jan. 2022), theaverage budget per user of an ERP -system is $9,000. On average, about 26% of the company’s employees use such systems. Thus, for an organization with 100 users, the total cost of ERP implementation reaches approximately $900,000.
Investments in proprietary, closed, modular solutions are becoming less and less justified against the backdrop of the rapid development of modern, flexible and open technologies. If such investments have already been made, it is important to objectively reevaluate the role of existing systems: whether they remain necessary in the long term, or whether their functions can be revised and implemented more efficiently and transparently.
One of the key problems with today’s modular data platforms is that they centralize data management within closed applications. As a result, data – a company’s primary asset – becomes dependent on specific software solutions, rather than the other way around. This limits information reuse, complicates migration and reduces business agility in a rapidly changing digital landscape.
If it is likely that the value or relevance of closed modular architecture will diminish in the future, it makes sense to recognize the costs incurred today as sunk costs and focus on a strategic shift to a more open, scalable and adaptive digital ecosystem.
Proprietary software is characterized by exclusive control by the development company over the source code and user data created as part of the use of such solutions. Unlike open source software, users do not have access to the internal structure of the application and cannot independently review, modify or adapt it to their needs. Instead, they are required to purchase licenses that grant the right to use the software within the limits set by the vendor.
A modern data-centric approach offers a different paradigm: data should be viewed as a core strategic asset – independent, durable and separate from specific software solutions. Applications, in turn, become mere data tools that can be freely replaced without the risk of losing critical information.
The development of ERP and MRP systems in the 1990s (Fig. 1.2-1) provided businesses with powerful tools for process management, but it also had the unintended consequence of significantly increasing the number of employees dedicated to maintaining information flows. Instead of automating and simplifying operational tasks, such systems often created new levels of complexity, bureaucracy and dependence on internal IT resources.