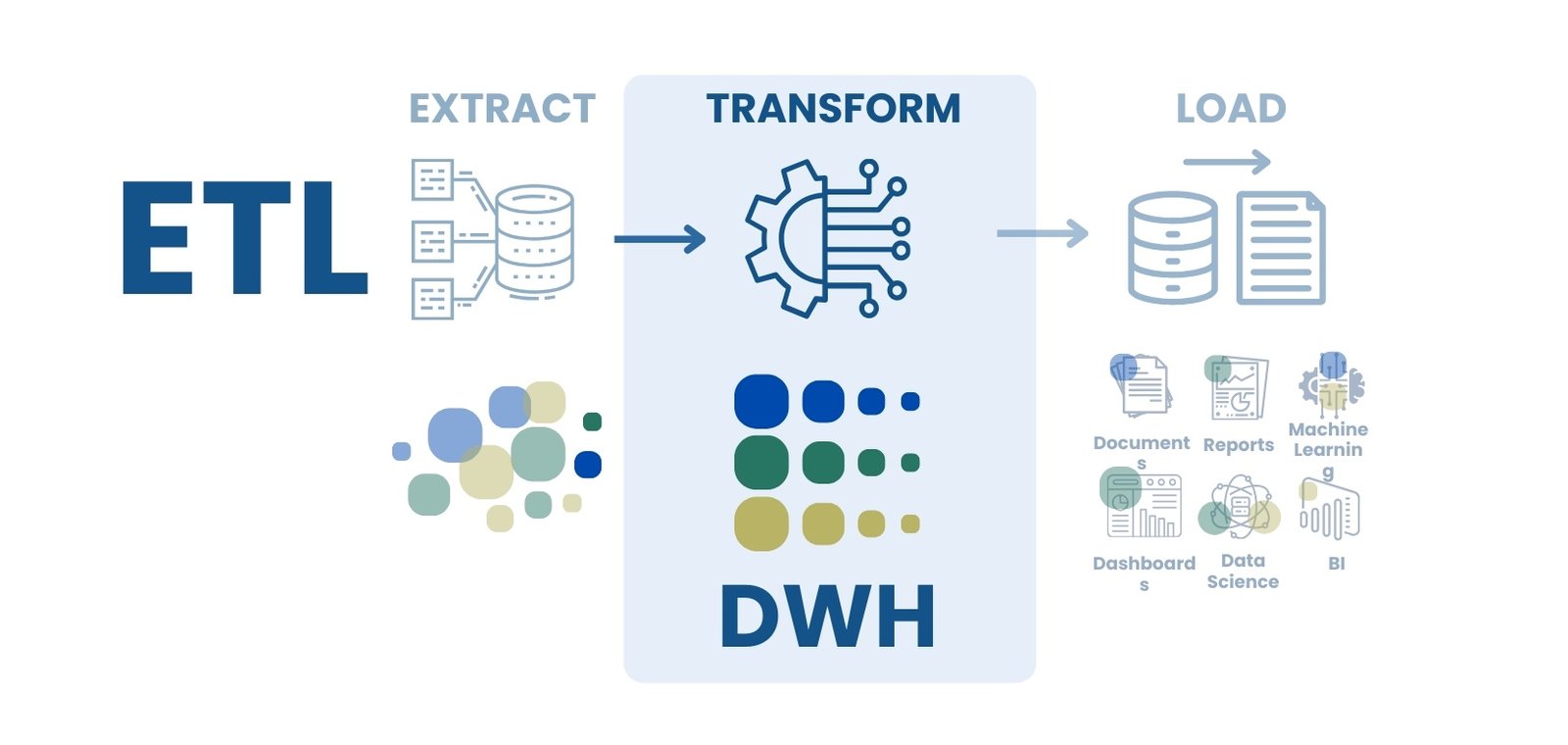
Just as the Parquet format is optimized for efficient storage of large amounts of information, the Data Warehouse is optimized for integrating and structuring data to support analytics, forecasting and management decision making.
In today’s companies, data comes from many disparate sources: ERP, CAFM, CPM, CRM systems, accounting and warehousing, digital CAD models of buildings, IoT sensors and other solutions. To get a holistic picture, it’s not enough to just collect data – it needs to be organized, standardized and centralized in a single repository. This is exactly what DWH does – a centralized storage system that allows you to aggregate information from various sources, structure it and make it available for analytics and strategic management.
DWH (Data Warehouse) is a centralized data warehouse system that aggregates information from multiple sources, structures it, and makes it available for analytics and reporting.
In many companies, data are scattered across different systems, which we discussed in the first parts of the book (Fig. 1.2-4). DWH integrates these sources, ensuring complete transparency and reliability of information. A DWH data warehouse is a specialized database (a large database) that collects, processes, and stores data from multiple sources. The main characteristics of a DWH are:
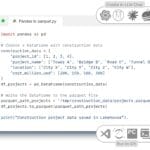
- Using ETL -processes (Extract, Transform, Load) – extracting data from sources, cleaning it, transforming it, loading it into the repository, and automating these processes discussed in Part 7 of the book.
- Data granularity – data in DWH can be stored in both aggregated form (summary reports) and in granular form (raw data). From 2024 onwards, it is CAD- vendors that have started talking about granular data (AECmag, “ADSK’s granular data strategy,” 25 Jul 2024), possibly indicating that the industry is preparing for the transition to specialized cloud storage for handling digital building model data.
- Supporting analytics and predictive analytics – data warehouses provide the foundation for BI tools, Big Data -analysis and machine learning.
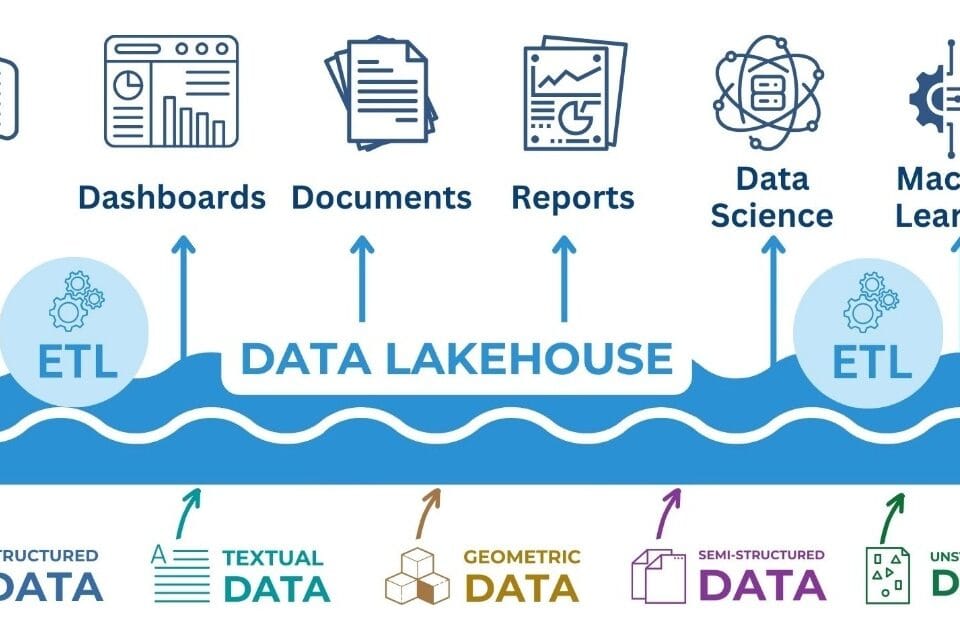
DWH serves as the foundation for business intelligence, enabling analysis of key performance indicators, forecasting of sales, purchases, and costs, and automated reporting and data visualization (Fig. 8.1-6).
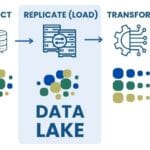
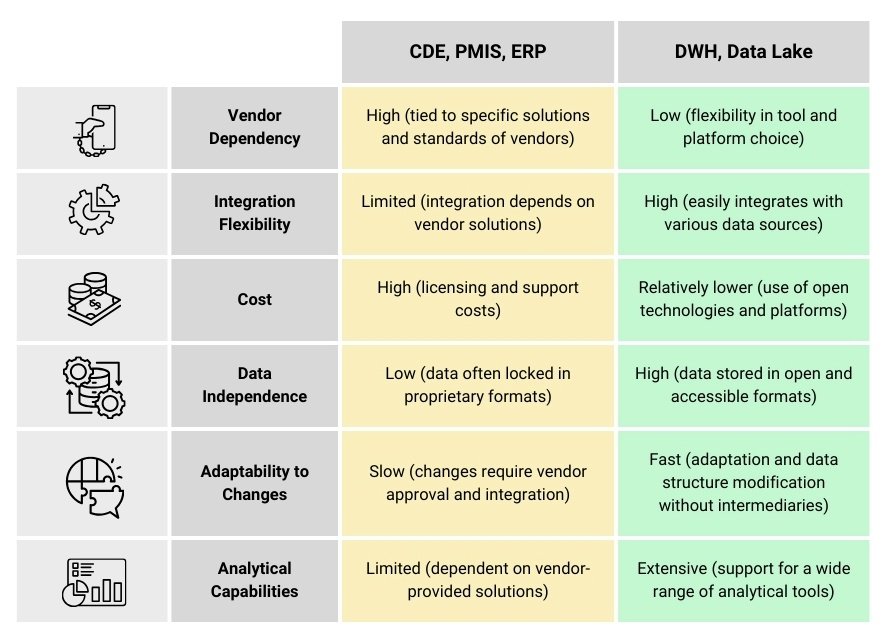
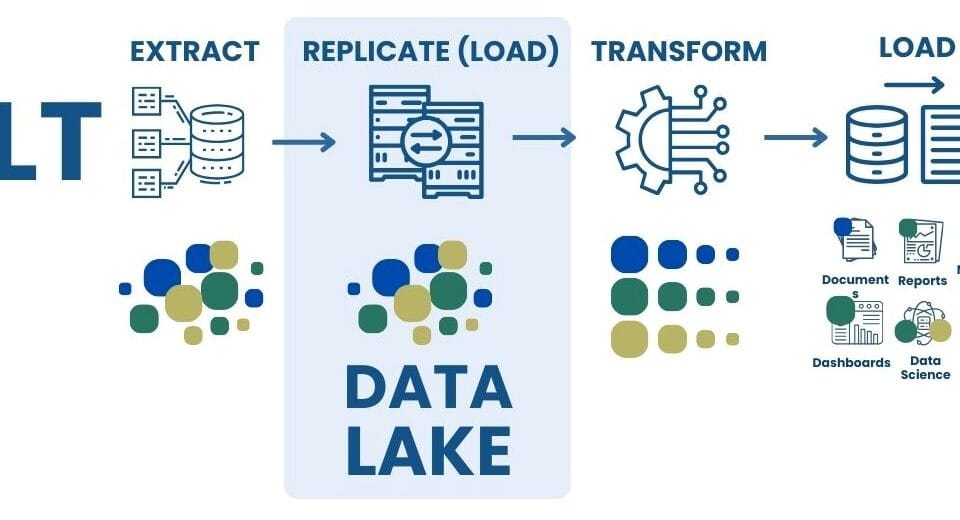
DWH plays a key role in integrating, cleansing and structuring information, providing a solid foundation for business intelligence and decision-making processes. However, in today’s environment where data volumes are growing rapidly and data sources are becoming increasingly diverse, the traditional DWH approach to information storage often requires extension in the form of ELT and Data Lake approaches