IoT The Internet of Things represents a new wave of digital transformation in which every device gets its own IP address and becomes part of a global network. IoT is a concept that involves connecting physical objects to the Internet to collect, process and transmit data. In construction, this means the ability to control construction processes in real time, minimize material loss, predict equipment wear and tear and automate decision-making.
According to the CFMA article “Preparing for the Future with Connected Construction“ (CFMA, “Preparing for the Future with Connected Construction”), the construction industry will undergo a major digital transformation in the next decade, culminating in the concept of Connected Construction – a fully integrated and automated construction site.
A digital construction site implies that all elements of construction – from planning and logistics to work execution and quality control at the construction site using fixed cameras and quadcopters – will be integrated into a single dynamic digital ecosystem. Earlier, in Part 7 of this book, we have already looked at the capabilities of Apache NiFi (Fig. 7.4-5), a free and open source tool that allows you to organize real-time data streaming – from collection from various sources to transfer to storage or analytics platforms.
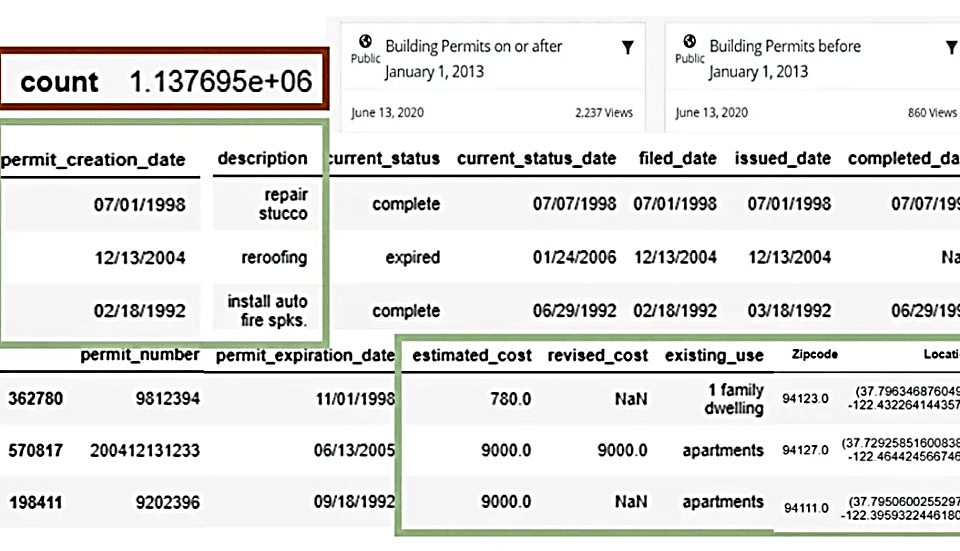
Data on construction progress, material consumption, equipment status and safety will be transmitted in real time to analytical systems (Fig. 9.1-13). This allows predicting potential risks, promptly reacting to deviations and optimizing site processes. Key components of a digital construction site include:
IoT -sensors – tracking environmental parameters, monitoring construction equipment and controlling labor conditions.
Digital twins – virtual models of buildings and infrastructure to predict possible deviations and prevent errors.
Automated logistics systems – real-time supply chain management to reduce downtime and costs.
Robotic construction complexes – using autonomous machines to perform routine and hazardous tasks.
Robotization use of IoT and the Connected Site (Construction) digital construction site concept will not just increase efficiency and reduce costs, but also usher in a new era of safety, sustainable construction and predictive project management.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags are also an important component of IoT. They are used to identify and track materials, machinery and even personnel on a construction site, increasing transparency and control of project resources.
RFID -technology is used to automatically recognize objects using radio signals. It consists of three key elements:
- RFID -tags (passive or active) – contain a unique identifier and are attached to materials, tools or machinery.
- Scanners are devices that read information from tags and transmit it to the system.
- Centralized database – stores information about the location, status and movement of objects.
Application of RFID in construction:
- Automatic material accounting – tags on ready-mixed concrete products, rebar or sandwich panel packages allow inventory control and prevent theft.
- Personnel work control – RFID – employee badges record shift start and end times, providing a record of working hours.
- Equipment Monitoring – RFID – system tracks the movement of equipment, preventing downtime and improving logistics efficiency.
Complementing this technology suite are blockchain-based smart contracts that automate payments, delivery control and contract compliance without the need for intermediaries, reducing the risk of fraud and delays.
Today, in the absence of a common data model, smart contracts are simply code that participants agree upon. However, with a Data-Centric approach, it is possible to create a common model of contract parameters, encode it in a blockchain, and automate the fulfillment of the terms.
For example, in a supply chain management system, a smart contract can track the delivery of a shipment from IoT -sensors and RFID -tags and automatically transfer payment when it arrives. Similarly, on a construction site, a smart contract can record the completion of a work phase – such as installing rebar or pouring a foundation – based on data from drones or construction sensors and automatically initiate the next payment to the contractor without the need for manual checks and paper certificates.
But despite new technologies and the efforts of international standardization organizations, a multitude of competing standards complicate the IoT landscape.
According to a Cisco study published in 2017 (Cisco, “Cisco Survey Reveals Close to Three-Fourths of IoT Projects Are Failing,” May 22, 2017), almost 60% of Internet of Things initiatives (IoT) stop at the proof-of-concept stage, and only 26% of companies consider their IoT projects to be fully successful. Moreover, a third of completed projects do not achieve their stated goals and are not recognized as successful even after implementation.
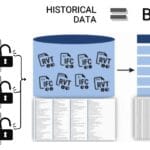
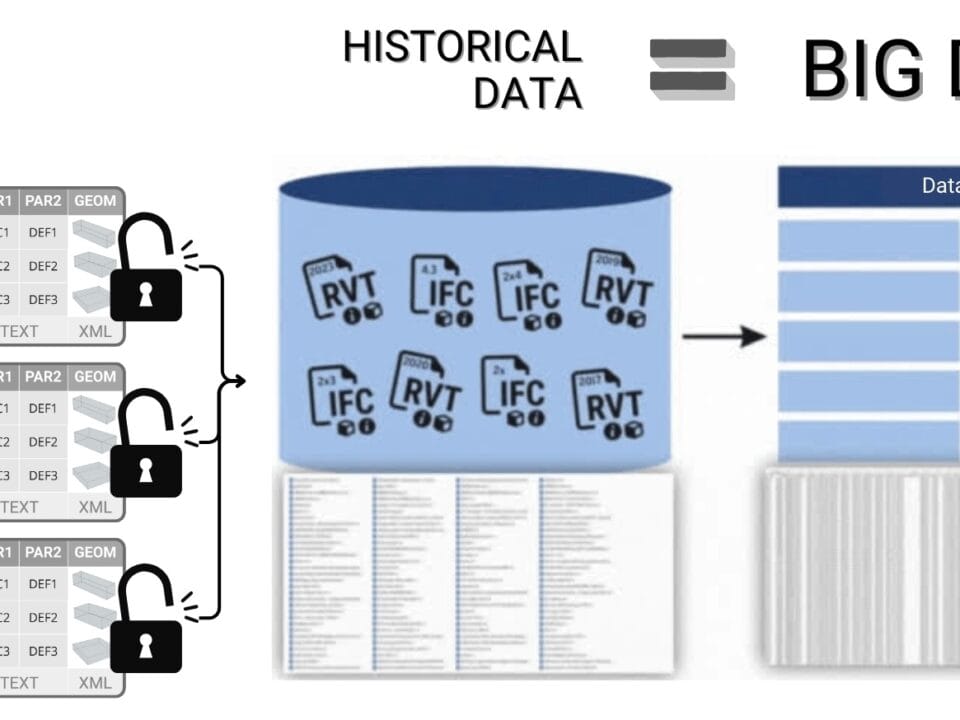
One of the key reasons is the lack of interoperability between platforms that process data from different sensors. As a result, data remains isolated within separate solutions. An alternative to this approach, as in other similar cases (which we have covered in this book), is an architecture built around the data itself as the primary asset.
IoT sensors play a key role not only in monitoring the technical condition of equipment, but also in predictive analytics to reduce risks on the construction site and improve overall process performance by predicting failures and deviations.
The data collected by IoT sensors and RFID tags can be processed in real time by machine learning algorithms that can detect anomalies and alert engineers to potential malfunctions in advance. This can range from micro-cracks in concrete structures to uncharacteristic pauses in tower crane operation, indicating technical failures or regulatory violations. Furthermore, advanced behavioral analysis algorithms can capture behavioral patterns that may indicate, for example, physical fatigue of personnel, enhancing proactive management of safety and employee well-being on site.
In the construction industry, accidents and failures – whether of machinery or people – rarely happen suddenly. They are usually preceded by minor deviations that go unnoticed. Predictive analytics and machine learning make it possible to detect these signals at an early stage, even before critical consequences occur.
While documents, project files, and data from IoT devices and RFID tags form the digital footprint of construction projects, machine learning can help extract useful insights from it. With the growth of data and democratization of data access, the construction industry is gaining new opportunities in analytics, predictive analytics and artificial intelligence applications.