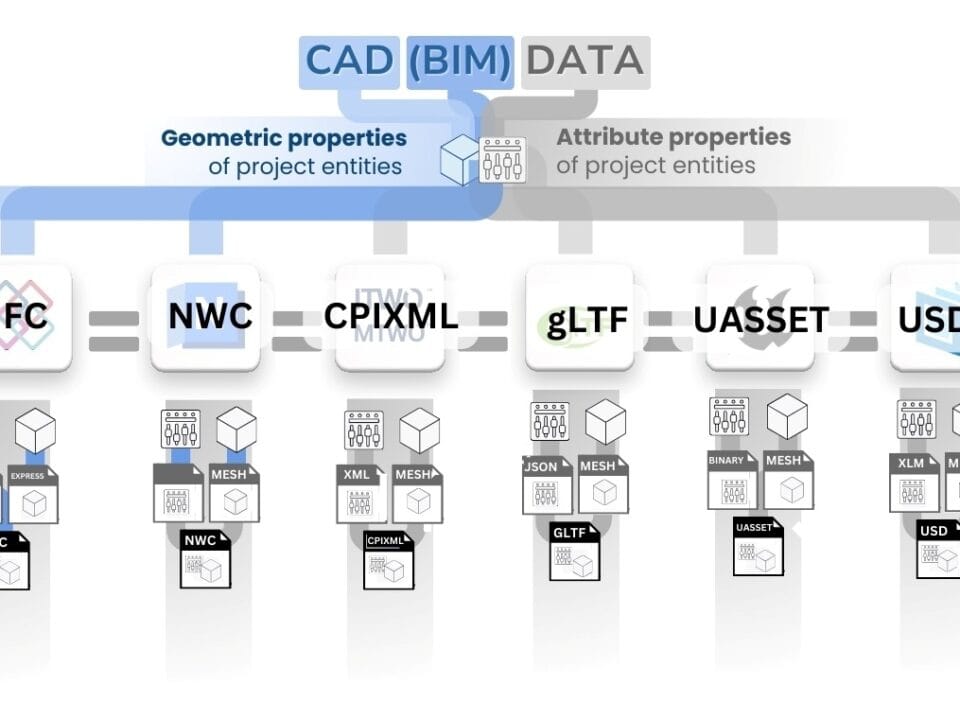
Although most of the data used in applications and information systems is in structured form, most of the information generated in construction is in the form of unstructured data – images, videos, text documents, audio recordings and other forms of content. This is especially true at the construction, operation and technical supervision stage, where visual and textual information predominates.
Unstructured data is information that has no predetermined model or structure, not organized into traditional rows and columns as in databases or tables.
In general terms, unstructured data can be classified into two categories:
- Human-generated unstructured data, which includes various types of human-generated content: text documents, emails, images, videos, and so on.
- Machine-generated unstructured data is created by devices and sensors: these include log files, GPS data, Internet of Things (IoT) results, and other telemetry information from a construction site, for example.
Unlike structured data, which are conveniently organized in tables and databases, unstructured data require additional processing steps before their integration into information systems (Fig. 3.1-8). The use of technologies for automated collection, analysis and transformation of such data opens up new opportunities for improving construction efficiency, reducing errors and minimizing the influence of human factor.
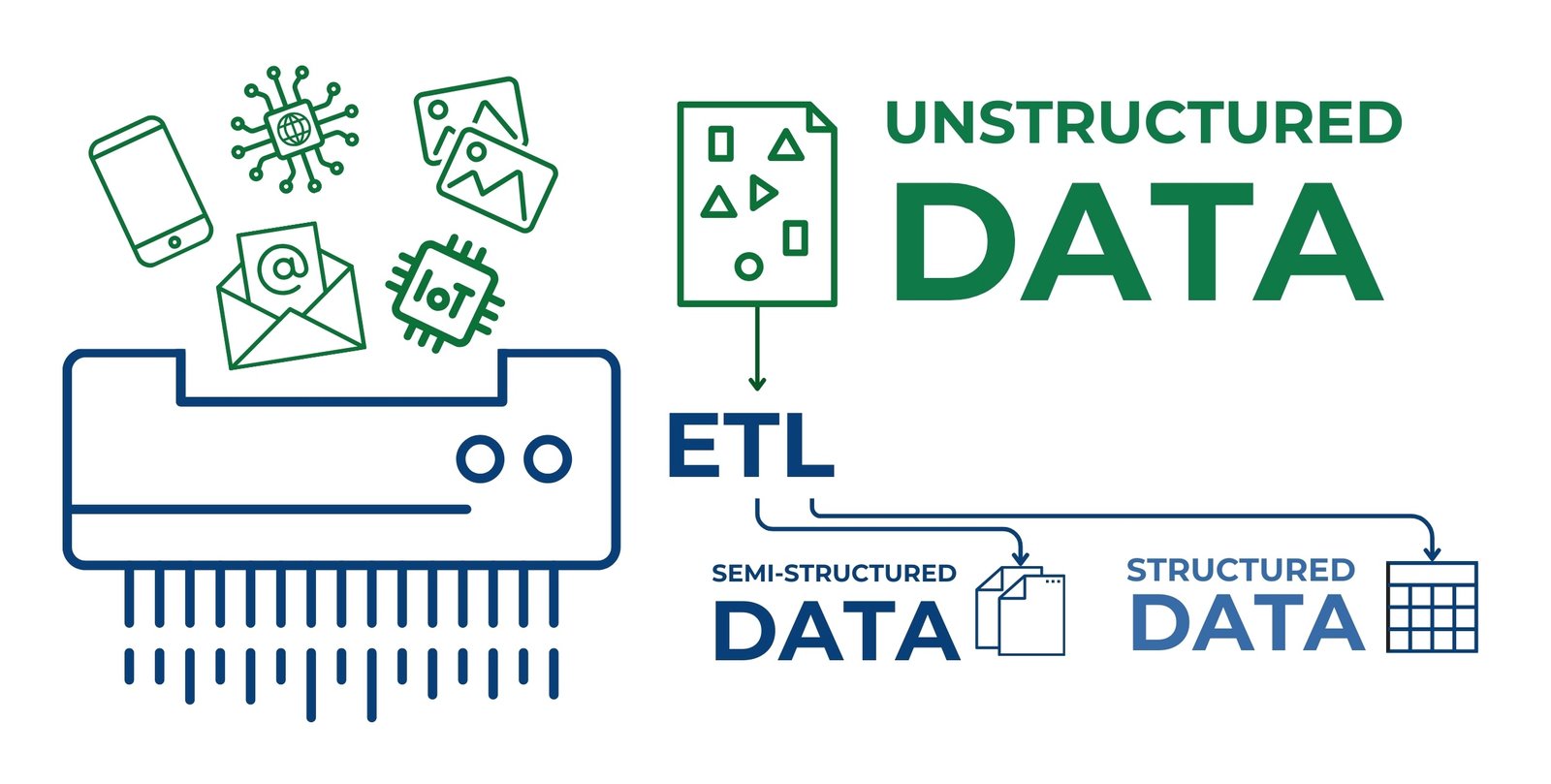
Unstructured data account for up to 80% of all information (“Structured and unstructured data: What’s the Difference?,” 2024)encountered by professionals in companies, so we will discuss their types and processing in detail with examples in the following chapters of the book.
For ease of discussion, we will separate textual data into a separate category. Although they are a type of rather unstructured data, their importance and prevalence in the construction industry require special attention.