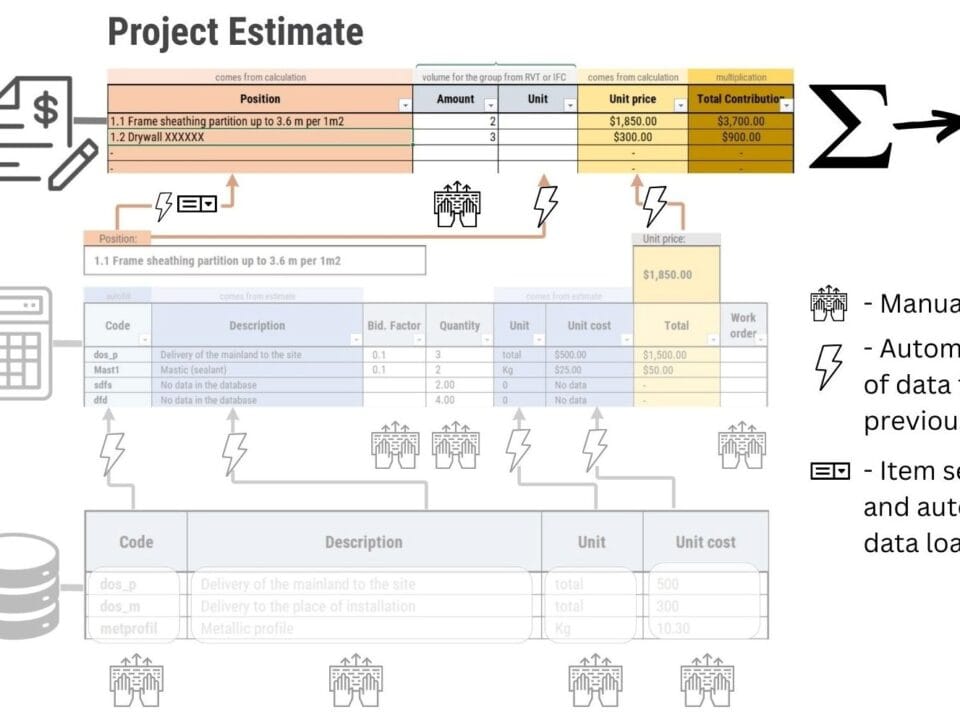
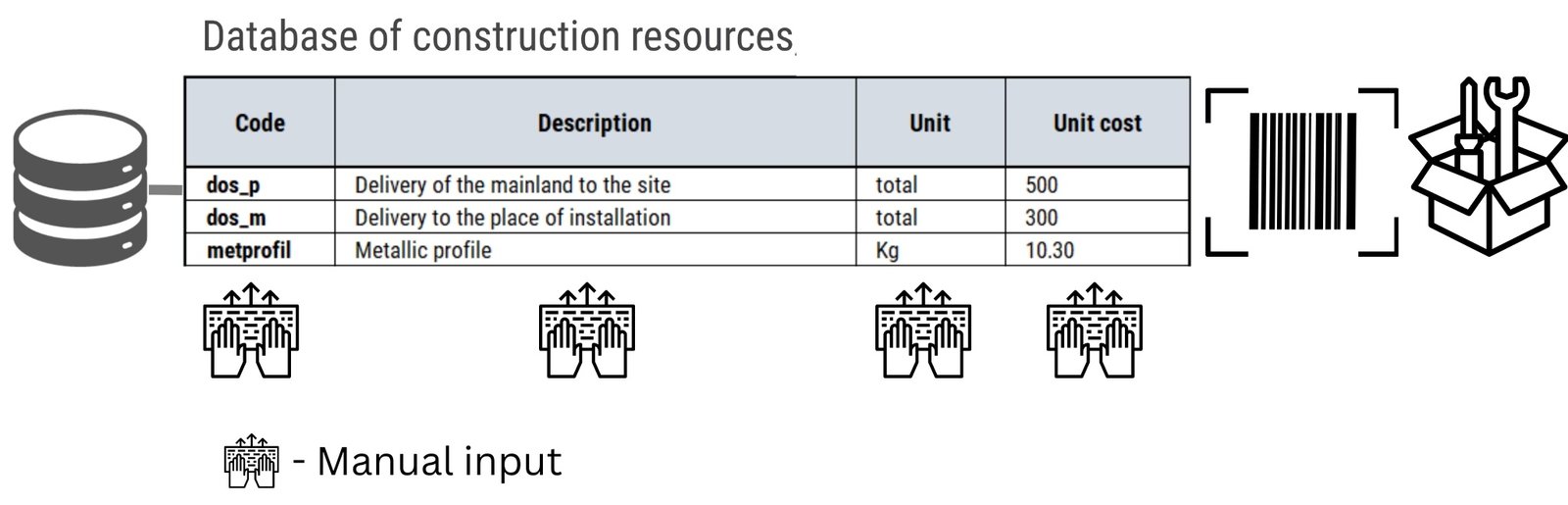
A database or table of construction resources and materials – includes detailed information about each element that can be used in a construction project – a commodity, product, material or service, including its name, description, unit of measurement and unit cost, recorded in a structured form. In this table you can find everything from different types of fuels and materials used in projects to detailed lists of specialists in the form of different categories with descriptions of hourly rates (Fig. 5.1-2).
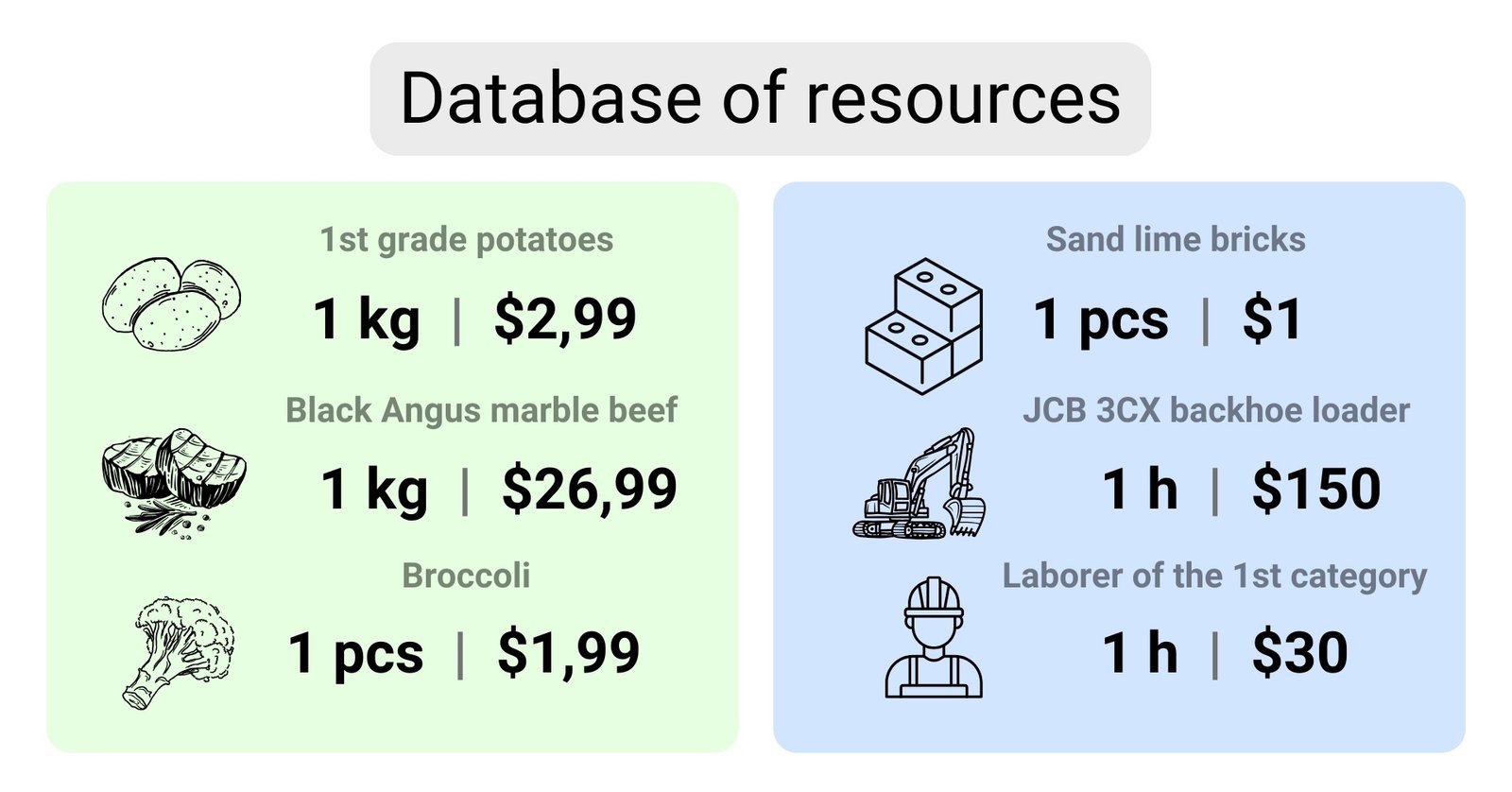
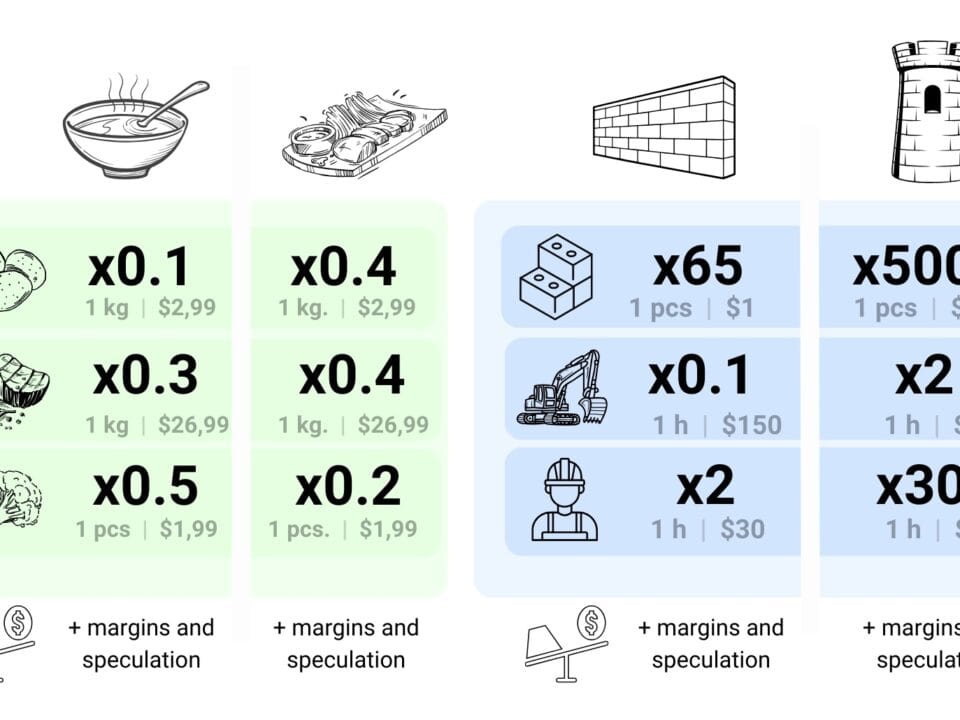
“Resource database” is akin to the product catalog of an online store, where each item has a detailed description of its attributes. This makes it easier for estimators to select the right resources (like selecting items when adding to a shopping cart) needed to calculate specific construction processes in the form of calculations (final order in the online store).
A resource database can also be thought of as a list of all the ingredients in a restaurant cookbook. Each building material, equipment and service is similar to the ingredients used in recipes. “Resource database” is a detailed list of all ingredients – building materials and services, including their cost per unit: piece, meter, hour, liter, etc.
New entity elements can be added to the “Construction Resource Databases” table in two ways – manually (Fig. 5.1-3) or automatically by integrating with the company’s inventory management systems or supplier databases.
A typical mid-sized construction company utilizes a database containing thousands, and sometimes tens of thousands, of items with detailed descriptions that can be used in construction projects. This data is then automatically used in contracts and project documents to accurately describe the work mix and processes
To keep up with changing market conditions such as inflation, the “unit cost” attribute for each product (good or service) in the resource database (Fig. 5.1-3) is regularly updated manually or by automatically downloading current prices from other systems or online platforms.
Updating the unit cost of a resource can be done monthly, quarterly or annually – depending on the nature of the resource, inflation and the external economic climate. Such updates are necessary to maintain the accuracy of calculations and estimates, as these basic elements are the starting point for the work of cost estimators. Up-to-date data is used to generate estimates, budgets and schedules that reflect real market conditions and reduce the risk of errors in subsequent project calculations.