In engineering practice, volumes and areas are computed from geometric surfaces described analytically or through parametric models such as NURBS (nonuniform rational B-splines) within the BREP (boundary element representation) framework.
NURBS (Non-Uniform Rational B-Splines) is a mathematical way of describing curves and surfaces, whereas BREP is a framework for describing the complete three-dimensional geometry of an object, including its boundaries, which can be defined using NURBS.
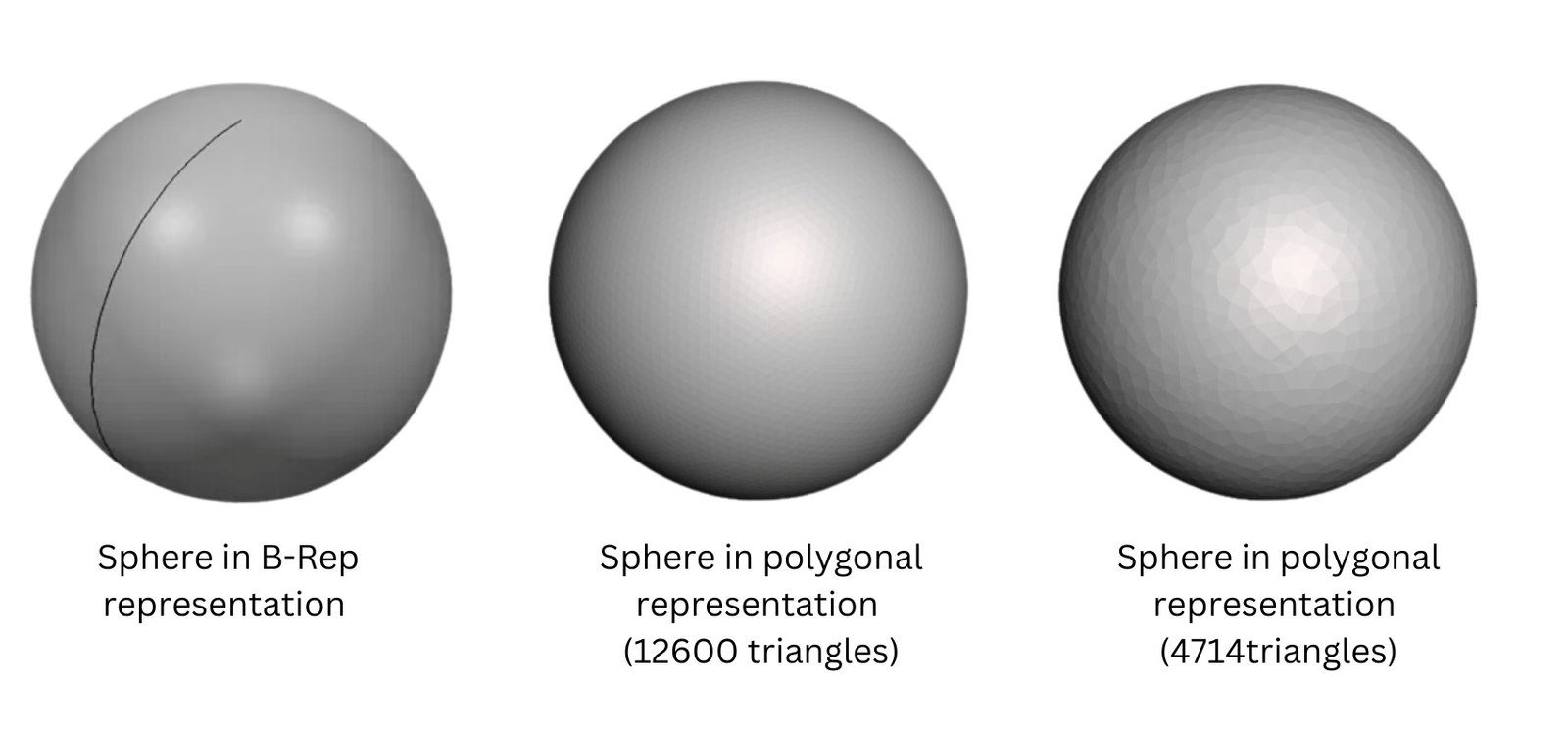
Despite the accuracy of BREP and NURBS, they require powerful computational resources and complex algorithms. However, direct computation from such mathematically accurate descriptions is often computationally difficult, so in practice, tessellation – the transformation of surfaces into a grid of triangles – is almost always used, which simplifies subsequent computations. Tessellation is the partitioning of a complex surface into triangles or polygons. In CAD /CAE environments this method is used for visualization, volume calculations, collision search, export to formats like MESH and collision analysis. An example from nature is bee honeycomb, where a complex shape is broken down into a regular grid (Fig. 6.3-1).
BREP (NURBS), used in CAD, is not a fundamental model of geometry. It was created as a convenient tool for representing circles and rational splines and for minimizing the storage of geometry data. However, it has limitations – for example, the inability to accurately describe the sinusoid that underlies helical lines and surfaces, and the need for complex geometry kernels.
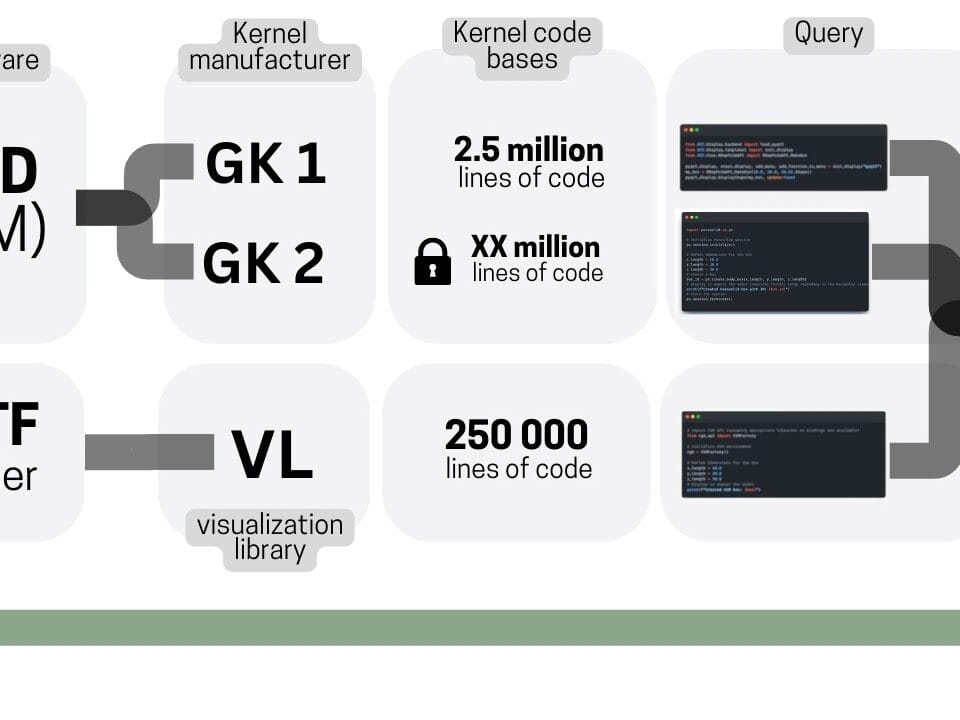
In contrast, triangular meshes and tessellation of parametric shapes are characterized by simplicity, efficient use of memory and ability to process large amounts of data (Fig. 6.3-2). These advantages make it possible to do without complex and expensive geometry kernels, and the tens of millions of lines of code embedded in them, when calculating geometric shapes.
In most building cases it does not matter how exactly the volumetric characteristics are defined – through parametric models (BREP, IFC) or through polygons (USD, glTF, DAE, OBJ). The geometry remains the form of approximation: whether through NURBS or MESH, it is always an approximate description of the shape.
Geometry defined as polygons or BREP (NURBS) remains to some extent only a way of approximating with an approximate description of a continuous form. Just as Fresnel integrals have no exact analytic expression, discretizing geometry through polygons or NURBS is always an approximation, just as triangular MESH.
Parametric geometry in BREP format is necessary mainly where minimal data size is important and it is possible to use resource-intensive and expensive geometry kernels for its processing and display. Most often it is characteristic for developers of CAD -programs, which for this purpose apply in their products geometrical kernels of MCAD -vendors. At the same time, even within these programs, BREP-models in the process of tessellation for visualization and calculations are often converted into triangles (similar to the way PSD-files are simplified into JPEG).
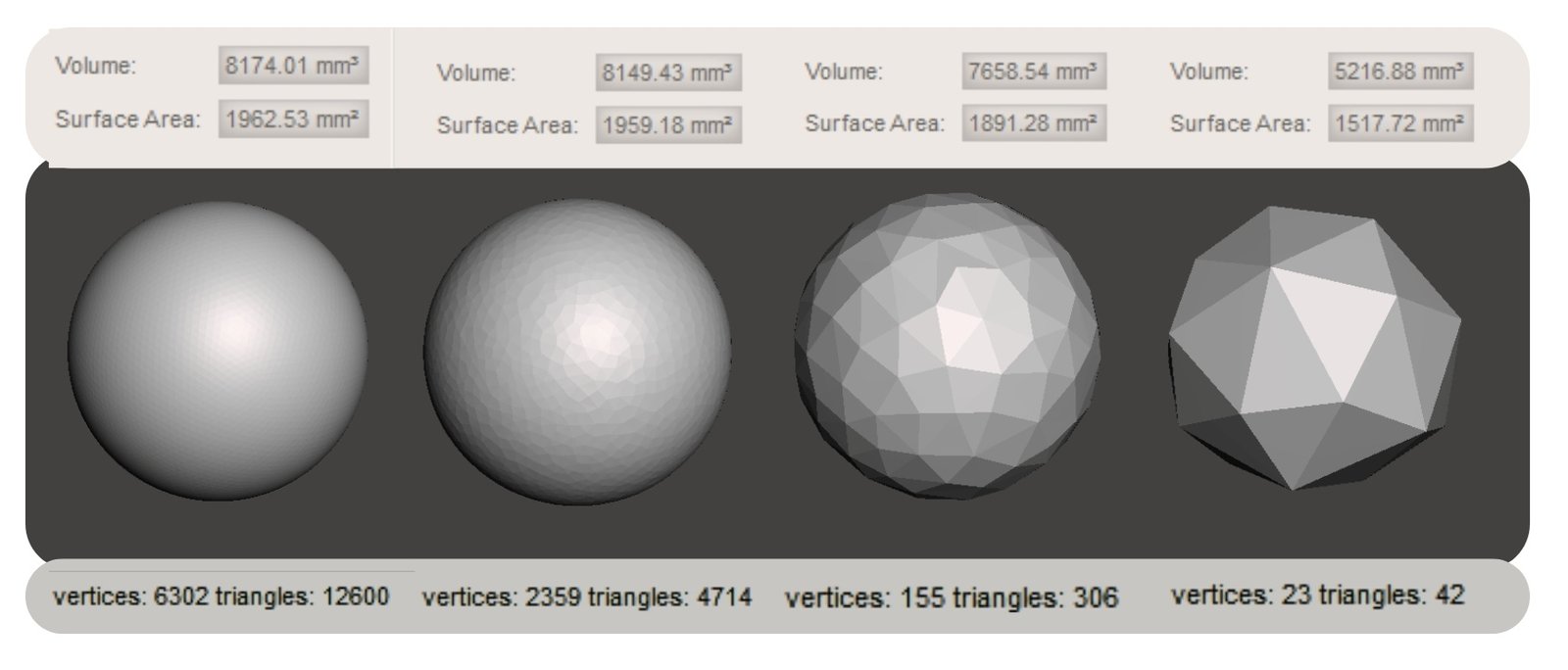
Polygonal MESH, as well as parametric BREP, have their own advantages and limitations, but the goal is the same – to describe the geometry taking into account the user’s tasks. Ultimately, the accuracy of a geometric model depends not only on the method of its representation, but also on the requirements of a particular task.
In most construction problems, the need for parametric geometry and complex geometric kernels may be redundant.
In each particular calculation automation task, it is worth considering whether the importance of parametric geometry is exaggerated by CAD developers who are interested in promoting and selling their own software products.